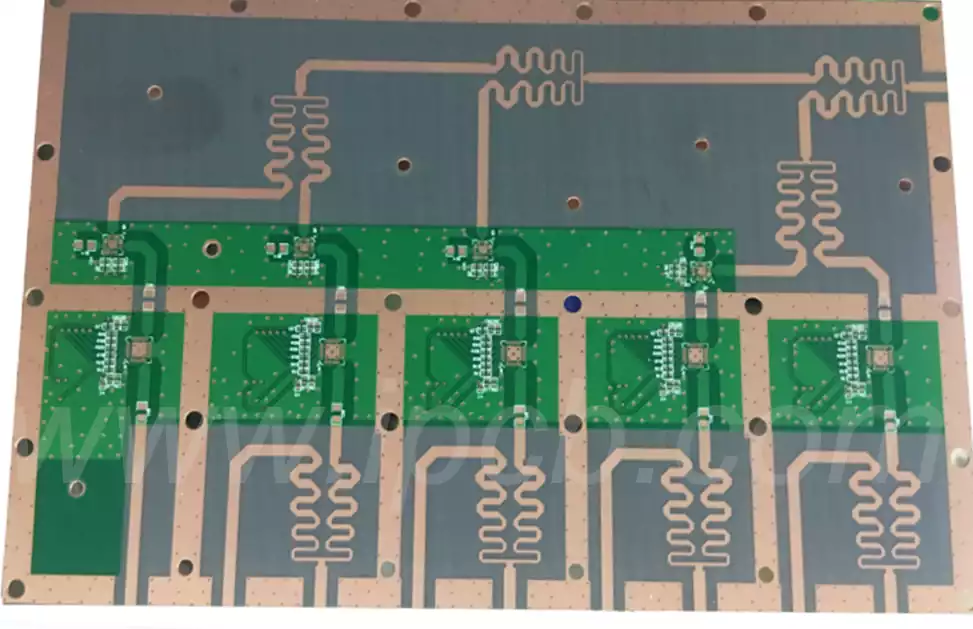
Microwave circuit board is a special kind of circuit board, which has good performance for the transmission of high-frequency signals. Compared to general printed circuit boards, it has a more unique circuit layer structure, commonly single, double and multilayer. Microwave circuit boards (high-frequency boards), refers to the specific microwave substrate copper-clad boards, the use of ordinary rigid printed circuit board manufacturing methods to produce microwave devices.
The manufacturing process of rf microwave circuit boards is complex and requires special materials and processes to meet the requirements of high frequency transmission. Common materials include Teflon and Rogers, which have low dissipation, low dielectric constant, low dielectric loss, high conductivity and other properties.
Microwave circuit board (high-frequency board) material selection
Microwave circuit board (high-frequency board) substrate selection should first consider its dielectric properties, but also must consider the surface of the copper foil type and thickness, environmental adaptability, processability and other factors, of course, there is also the issue of cost.
Selection of copper foil type and thickness
The most commonly used copper foil thicknesses are 35μm and 18μm. The thinner the copper foil, the easier it is to obtain a high degree of graphic precision, so high-precision microwave graphics should not be greater than 18μm copper foil. If the choice of 35μm of copper foil, the high precision of the graphics to make the process worse, the failure rate is bound to increase.
Research shows that the type of copper foil also has an impact on the graphic accuracy. Currently, there are two types of copper foils: calendered copper foil and electrolytic copper foil. Calendered copper foils are more suitable for high precision graphics than electrolytic copper foils, so when ordering materials, consider selecting calendered copper foils for the substrate board.
Environmental Adaptability Selection
Existing microwave substrates, for the standard requirements of -55 ℃ ~ +125 ℃ ambient temperature range are no problem. However, two points should also be considered, one is the impact of porosity on the choice of substrate, for the requirements of through-hole metallization of microwave circuit boards, substrate Z-axis coefficient of thermal expansion of the larger, meaning that in the high and low temperatures under the impact of the metallization of holes in the greater the possibility of fracture, and thus in order to meet the dielectric properties of the premise, should be as far as possible, select the Z-axis coefficient of thermal expansion of the substrate of the small (see Table I to Table IV); the second is the impact of humidity on the choice of substrate plate, the substrate resin itself is very small water absorption, the substrate is very small. Substrate resin itself is very small water absorption, but after adding reinforcing materials, the overall water absorption increases, in the use of high humidity environment will have an impact on the dielectric properties, so the selection of materials should be selected to absorb small substrate (see Table I to Table IV), or to take structural measures to protect the process.
Selection of processability
As design requirements continue to improve, some microwave printed circuit board substrates with aluminum liner. The presence of such aluminum-lined substrates puts additional pressure on the manufacturing process, complicating the graphic production process, complicating the shape processing, and lengthening the production cycle time, so that substrates with aluminum liners are not used if they are available or not.
ROGERS’ TMM series microwave circuit board substrates are made of ceramic powder-filled thermosetting resin. Among them, the TMM10 substrate is filled with more ceramic powder and has brittle properties, which makes the graphic manufacturing and profile machining process very difficult, and is prone to defects or the formation of intrinsic cracks, with a relatively low yield rate. At present, the shape processing of TMM10 plate is by laser cutting method, which is costly, inefficient and has a long production cycle. Therefore, if possible, consider giving preference to the RT/Duroid series substrate boards from ROGERS, which meet the corresponding dielectric property requirements.
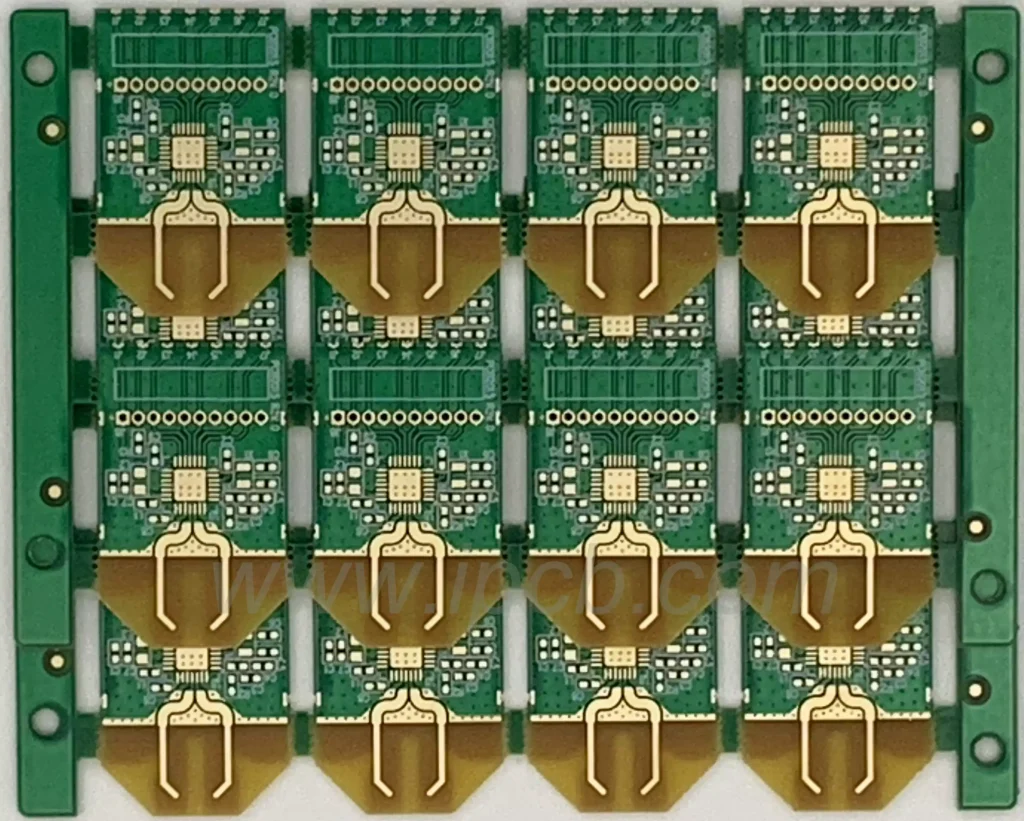
Applications of Microwave substrate
- Communications
The application of microwave circuit boards in the field of communication is mainly concentrated in the field of cellular phones and mobile communication base stations. It can be used as a connection between the transmitter and receiver to realize the transmission of high-frequency signals in communication. At the same time, the microwave circuit board can also realize the connection between antenna and receiver. - Radar field
Microwave circuit boards are widely used in the field of radar. Radar system needs to go through the signal modulation, transformation and demodulation and other processing, microwave circuit board is to realize the key components of these processes. It can realize high-speed transmission of electron beams between radar transmitters and antennas. - Satellite communication field
High-speed transmission is required in the field of satellite communication, and microwave circuit boards can realize high-frequency and high-speed transmission, so they are widely used in the field of satellite communication. It can be used as the connection between the satellite and the ground station to realize high-speed data transmission. - Aerospace field
Microwave circuit boards are also quite widely used in the aerospace field. In the aircraft, it is able to connect between the aircraft and the ground base station through the microwave circuit board to realize high-speed communication.
As an indispensable core component in modern communications, radar, satellite communications and aerospace, microwave circuit board provides a solid guarantee for the transmission of high-frequency signals due to their high precision, high reliability and high performance. With the continuous progress of science and technology and the increasingly wide range of applications, microwave circuit boards will continue to pursue higher precision, lower loss and stronger environmental adaptability in design and manufacturing.