With the rapid advancement of semiconductor lighting technology, high-power LEDs have gained widespread application in road lighting, industrial illumination, automotive lighting, and specialised lighting sectors due to their high luminous efficacy, extended lifespan, and energy-saving advantages. However, as power levels continue to increase, thermal management has emerged as the core bottleneck constraining the performance and reliability of high-power LEDs. Against this backdrop, ceramic circuit boards (Ceramic PCB) have emerged as the mainstream solution in high-end LED packaging and module design, owing to their superior thermal management capabilities.
During operation, high-power LEDs convert only approximately 30%–40% of electrical energy into light energy, with the majority of the remaining energy concentrated as heat within the PN junction region. Failure to dissipate this heat promptly leads directly to the following issues:
Increased junction temperature, accelerated lumen depreciation, and significantly reduced LED lifespan
Diminished luminous efficacy, colour temperature drift, and compromised lighting quality
Thermal stress on encapsulation materials and solder joints, leading to diminished reliability
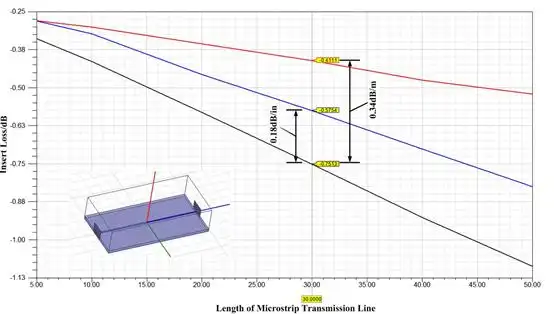
Conventional FR-4 PCBs or metal-clad laminates (MCPCBs) in high-power-density applications are often constrained by lengthy thermal pathways and substantial interfacial thermal resistance, struggling to meet stringent thermal dissipation requirements.
Material Advantages of Ceramic Circuit Boards
1.High thermal conductivity, establishing low thermal resistance dissipation pathways
During LED operation, the chip junction area continuously generates substantial concentrated heat. The thermal conductivity of the substrate material directly determines whether heat can be rapidly conducted and dispersed.
Alumina ceramics typically exhibit thermal conductivities of 20–30 W/(m·K), substantially exceeding the approximately 0.3 W/(m·K) of conventional FR-4 substrates. Aluminium nitride ceramics achieve even higher thermal conductivities of 170–200 W/(m·K), approaching levels of certain metallic materials.
This high thermal conductivity enables ceramic circuit boards to rapidly dissipate heat from beneath the LED chip along extremely short paths, substantially reducing thermal resistance and temperature rise while effectively controlling junction temperature. Simultaneously, the rapid diffusion of heat within the substrate helps prevent localised hotspots, thereby enhancing the thermal stability of the entire luminaire or module.
2.Concurrent electrical insulation and high thermal conductivity minimise interfacial heat loss
Unlike metal-clad polyimide circuit boards (MCPCBs), ceramic materials inherently possess both excellent electrical insulation and thermal conductivity. Within ceramic circuit board structures, circuit layers can be directly and tightly bonded to the ceramic substrate without requiring additional insulating layers.
This characteristic holds significant importance for thermal management:
Traditional MCPCBs rely on insulating layers for electrical isolation, yet these layers often exhibit limited thermal conductivity, becoming a primary bottleneck in the overall heat dissipation pathway;
Ceramic substrates achieve electrical insulation through the material itself, significantly reducing thermal resistance accumulation caused by interlayer structures.
Consequently, heat can be conducted to the heat sink or external environment via shorter, more direct pathways, enhancing overall thermal efficiency at the system level.
3.Superior thermal expansion matching enhances long-term reliability
In practical high-power LED applications, devices endure repeated power cycling and environmental temperature fluctuations over extended periods. Thermal expansion mismatch is a key factor contributing to solder joint fatigue, chip cracking, and package failure.
The linear thermal expansion coefficient of ceramic materials closely matches that of GaN (gallium nitride), commonly used in LED chips, significantly outperforming metal or organic substrates. This excellent compatibility effectively reduces:
Mechanical stress between the chip and substrate
Shear fatigue within the solder layer
The risk of micro-cracks within the encapsulation structure
Thereby significantly enhancing the long-term reliability and service life of LED modules under high-power, high-temperature conditions.
4.Providing a Material Foundation for High-Power, High-Reliability Applications
Combining high thermal conductivity, electrical insulation, and thermal expansion matching, ceramic circuit boards offer a more stable and efficient operational platform for high-power LEDs at the material level. This not only aids in reducing junction temperature and enhancing luminous efficacy but also facilitates higher power density and more compact structural designs. As such, ceramic circuit boards serve as the fundamental material for achieving a balance between performance and reliability in high-end lighting and specialised applications.

Mechanism of Ceramic Circuit Boards in Thermal Pathways
Within high-power LED systems, the typical thermal pathway is:
Chip → Solder layer → Circuit board → Heat sink → Ambient environment
Within this pathway, ceramic circuit boards serve as a critical ‘high-efficiency thermal conduit’:
- Enabling rapid lateral and vertical heat diffusion through the intimate bonding of thick copper circuits with the ceramic substrate
- Significantly reducing the junction-to-board-bottom temperature differential, thereby enhancing overall thermal conduction efficiency
- Minimising reliance on complex cooling structures (e.g., heat pipes, air cooling) and simplifying system design
Ceramic circuit boards effectively resolve high-power LED thermal management challenges at both material and structural levels through high thermal conductivity, low thermal resistance, excellent compatibility, and high reliability. As manufacturing processes mature and costs progressively optimise, ceramic circuit boards will see broader adoption in high-end lighting and power electronics, providing robust support for unleashing high-power LED performance and ensuring stable system operation.