Flexible printed circuits (FPC), also known as flexible circuit boards, stand out in the electronics sector due to their high wiring density, lightweight and slim profile, and exceptional bending performance, making them highly favoured within the industry. These unique advantages enable FPCs to adapt flexibly to various complex shapes and size requirements, proving particularly suitable for applications demanding high flexibility and constrained by limited space. FPCs primarily encompass the following four common types:
Single-sided Flexible Circuit Board
The single-sided flexible circuit board occupies a significant position across numerous applications due to its lowest cost advantage. It is most suitable for scenarios with modest electrical performance requirements where circuitry can be routed on a single side. This board comprises a conductive pattern formed through chemical etching, adhered to the surface of a flexible insulating substrate. Rolled copper foil is typically selected as the conductive material. A diverse range of insulating substrates are available for flexible assembly, including polyimide (Kapton), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), aramid fibre paper (Nomex), and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Within commercial applications, this single-sided flexible circuit board has seen widespread adoption, appearing in products such as printer cartridges and computer memory modules.
Double-sided Flexible Circuit Boards
The defining characteristic of double-sided flexible circuit boards lies in the conductive patterns etched onto both sides of the insulating base film. Metallised vias connect the patterns on either side of the insulating material, forming reliable conductive pathways that fulfil the requirements for flexible design and functional implementation. Furthermore, the cover film not only protects both single- and double-sided conductors but also clearly indicates component mounting positions, facilitating circuit board assembly. Double-sided flexible boards find extensive application across numerous sectors, including digital cameras, handheld devices, liquid crystal displays, medical equipment, and industrial control systems.
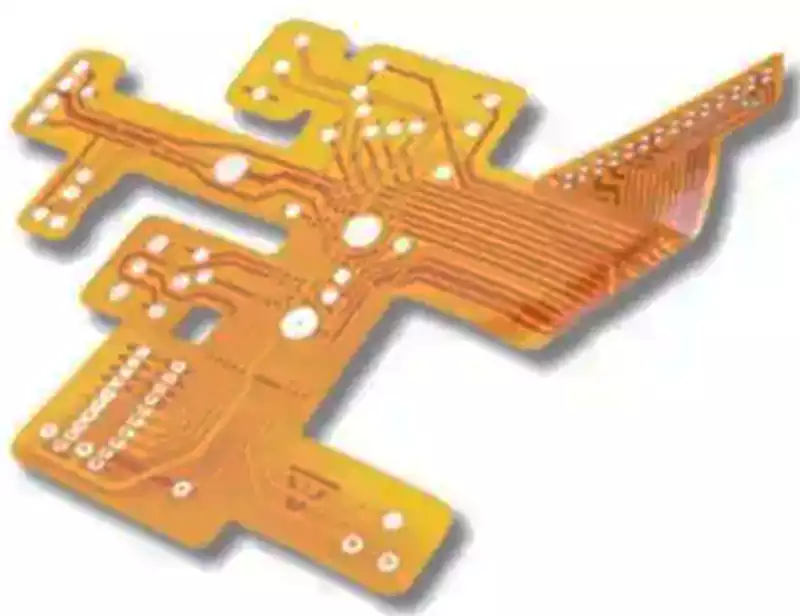
Multilayer Flexible Printed Circuits
Multilayer flexible circuit boards are manufactured by laminating three or more layers of single-sided or double-sided FPCs. Via holes formed through drilling and plating techniques establish conductive pathways between layers, effectively eliminating complex soldering processes. While theoretically capable of incorporating an unlimited number of conductive layers, practical design layouts must balance assembly dimensions, layer count, and the mutual influence between flexible layers to ensure assembly feasibility. Multilayer circuit boards demonstrate significant advantages in reliability, thermal conductivity, and assembly performance. Multilayer FPCs are commonly employed in high-end electronic products across mobile devices, medical equipment, automotive systems, and smart home applications, undertaking critical functions such as data transmission, signal processing, control, and power supply.
Rigid-Flex Circuit Boards
Traditional rigid-flex circuit boards combine rigid and flexible substrates through selective lamination. This structure offers high integrity and reliability, with conductive connections achieved via plated-through holes, ensuring stable circuit operation. Manufacturers typically minimise the number of layers during production to strike an optimal balance between reliability and cost.
HDI Rigid-Flex Boards: High-Density Interconnect (HDI) rigid-flex printed circuit boards fall within the high-end product category. Their design originates from the urgent demand for miniaturisation, high-frequency/high-speed capabilities, and multifunctionality in electronic products. HDI rigid-flex boards ingeniously integrate the advantages of HDI boards and rigid-flex boards -flex boards, significantly advancing electronic system design and manufacturing towards higher integration and intelligence. Currently, this technology finds extensive application in high-end electronics such as aerospace, medical equipment, and consumer products.
Each of the four types of flexible circuit boards possesses distinct characteristics, catering to diverse application requirements across different sectors. As electronic technology continues its steady advancement, these boards will undergo ongoing optimisation, providing reliable support for the stable operation of various electronic products.