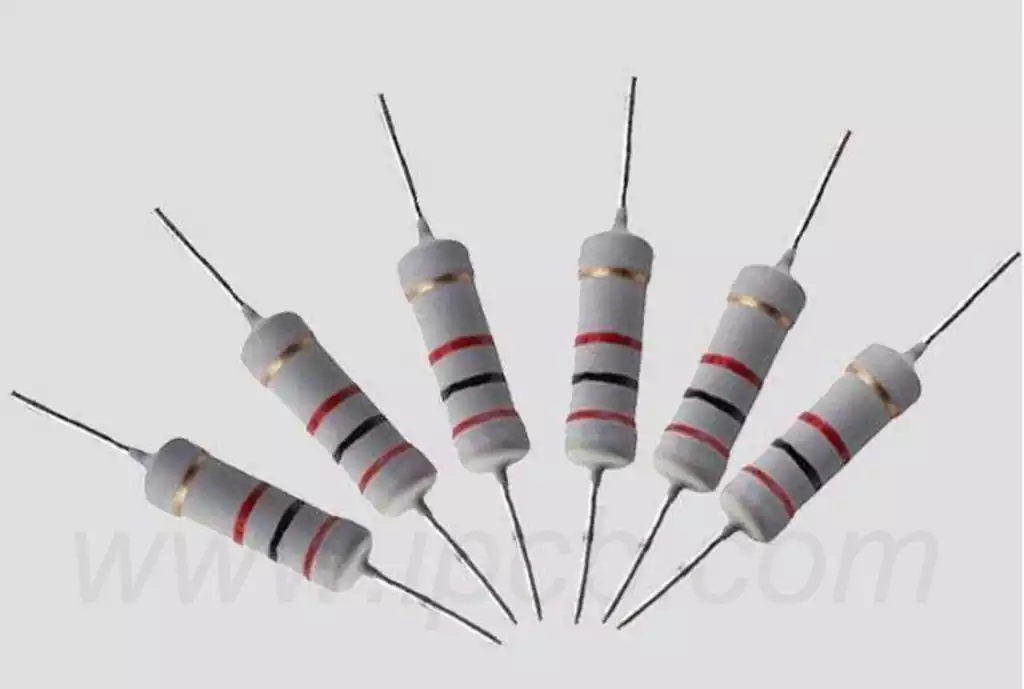
What is resistance in a circuit?Resistance ,usually denoted by “R”,is a physical quantity that, in physics, indicates the magnitude of a conductor’s resistance to electric current. The greater the resistance of a conductor, the greater the resistance of the conductor to the current. Resistance generally varies from conductor to conductor, and resistance is a property of the conductor itself. And the main roles of resistors on circuits are current-sharing, current-limiting, voltage-sharing, biasing, filtering (used in combination with capacitors), impedance matching, and converting electrical energy into internal energy.
Resistors can be categorized according to different criteria, including different ways of categorization according to structure, material, and use. Through this categorization, the functional characteristics of resistors and their applications in circuits can be better understood.
1.Classification by type
Resistors can be classified into three main categories: fixed resistors, adjustable resistors and special resistors. Among them, fixed resistors are the most commonly used type, and their resistance value is fixed after production. Adjustable resistors allow the user to adjust the resistance value as needed to suit the different requirements of the circuit.
2.Classification by Material
Resistors can also be categorized according to their manufacturing materials, such as carbon film resistors, metal film resistors, wirewound resistors and oxide film resistors. Resistors of different materials have different characteristics, such as temperature coefficient, stability and frequency characteristics.
3.Classification by Function
According to the function of the resistor, specialty resistors can be further classified into sensitive resistors, such as thermistors, photosensitive resistors, moisture-sensitive resistors, etc. These resistors are capable of making active responses to environmental changes. These resistors are able to react actively to environmental changes, and their resistance value will change with the change of temperature, light and other factors.
4.Other Classification
Resistors can also be categorized into linear and non-linear resistors based on their performance characteristics. Linear resistors remain basically unchanged within a certain current range, while non-linear resistors exhibit different resistance values at different voltages or currents, and are suitable for over-voltage protection.
Resistors in different circuits
Resistance AC signal voltage supply circuit
From the audio circuit output AC signal (audio signal), respectively, through the resistance R1 and R2 added to the left and right channels, so that the AC signal can be equalized into two signals, respectively, added to the left channel circuit and the right channel circuit, so that their amplification of the same signal, R1 and R2 resistance value is the same.
Resistance circuit in the negative feedback
Negative feedback circuit is also widely used, in the following circuit, when the transistor Q2 work in the amplified state, the need to add a suitable size of the DC voltage at the base of Q2 in order to produce a suitable size of the base current, resistor R2 plays this role, Q2 base is the signal input, collector output, R2 is connected to the base of Q2 and the collector between the components so that constitute a negative feedback circuit. Negative feedback circuit.
Resistance triode shunt application
Resistance shunt can reduce the burden of another component, here R1 shunt is very good to protect the triode is conducive to increasing the service life of the component. In the following circuit R1 is a shunt resistor, it is connected in parallel in the collector of Q1 and the emitter so that between them, forming a parallel circuit, part of the current in the circuit flows through R1, so that the current flowing through the Q1 is relatively reduced, while the total current does not change.
Damping resistance circuit
Circuit L1 and C1 constitute LC parallel resonant circuit, resistance RL2 is connected in parallel in the circuit to play the role of damping, L1 and C1 constitute the parallel resonant circuit, the resonant signal energy loss is very small, the resonant circuit of the quality factor of the larger the Q value. Since the resistor is an energy-consuming element, there is a loss of the oscillating signal, so add the damping resistor RL2 after the Q value will decrease, the smaller the resistance value of RL2 the greater the loss of the resonant signal.
Application of sampling resistor in the circuit
Sampling resistor is also commonly used in the power amplifier overcurrent protection sampling resistor. When the transistor Q2 transmitter circuit flows through the R2 will produce a voltage drop, the greater the current flows through the R2, the greater the voltage drop on the R2, the greater the voltage on the R2 represents the greater the current flows through the R2, so that the circuit of the overcurrent protection circuit will be acted on, to prevent the current from damaging the components in the circuit.
Pull-down resistor
This is the circuit of the inverter, the input signal is grounded through the pull-down resistor R1, so that in the absence of high level input, you can make the input stable in the low level state, to prevent possible high level interference that makes the inverter inaccurate, if there is no pull-down resistor R1 inverters hanging for high impedance, the outside world’s high level can easily interfere with the input to the inverter from the input side, which causes inaccurate operation.
The role played by two resistors in parallel
In some circuits are often seen in parallel with the use of some of the resistors, would have been a resistor can be dealt with why to connect two resistors in parallel in the circuit instead of a resistor, this is not more than one move? Next, we will talk about two parallel resistors in the circuit can actually play a big role. Such as the following circuit, two resistors used in parallel, can share part of the current, each sharing half of the current so that each resistor flow of current is half the small current, the current is small resistance of the heat is also small, while the two resistors also increase the heat dissipation area, the stability of the circuit for long periods of time also plays a big role in the stability of the work.
In the selection of resistors, the choice of materials on the circuit performance impact
Influence of Material Selection on Circuit Performance
When selecting a resistor, the difference in material will directly affect the conductivity, stability, and operating temperature range of the resistor and other key parameters. For example, metal resistors typically have lower resistivity and provide better conductivity, while carbon resistors are superior in terms of cost and stability, but may not perform well at high temperatures. This means that the choice of material must not only consider the resistance value of the resistor, but also its suitability and reliability for a particular application.
Importance of Temperature Coefficient
The temperature coefficient of different materials also has a significant effect on the performance of a resistor. For example, metal resistors typically have a positive temperature coefficient, meaning that their resistance value increases as the temperature rises, while carbon resistors may have a negative temperature coefficient characteristic. Such characteristics determine the stability of the resistor in high temperature environments and its range of applications, so the temperature coefficient must be carefully evaluated when designing circuits.
Power Rating and Voltage Withstand
The choice of material also affects the power rating and voltage capability of the resistor. Choosing the right material ensures that the resistor will operate safely within the expected power range, avoiding overheating and failure. For example, cement resistors are commonly used in high power applications, while metal film resistors are often used for precision measurements. Proper selection of resistor material and type can avoid circuit failures caused by inadequate heat dissipation.
Influence on Signal Steady State and Metastability
Material properties also affect a resistor’s ability to process signals, which is especially important in high-speed and low-frequency signal applications. Certain materials such as film resistors possess lower noise and better frequency response, making them suitable for high frequency signal processing, while wirewound resistors possess excellent temperature stability, making them suitable for applications requiring high stability.
In circuit design, the choice of resistor has a profound effect on the overall performance. Resistors of different materials in the conductivity, temperature coefficient, power rating and voltage withstand capacity, etc., each with its own characteristics, these characteristics are not only related to the stability and reliability of the circuit, but also affect the application of the circuit in different environments. Therefore, engineers need to consider a variety of factors when selecting resistors to ensure that the selected resistance can meet the needs of specific applications, while enhancing the overall performance and safety of the circuit. Understanding the diversity of resistors and their multiple roles in circuits is the foundation for building high-quality electronic products.