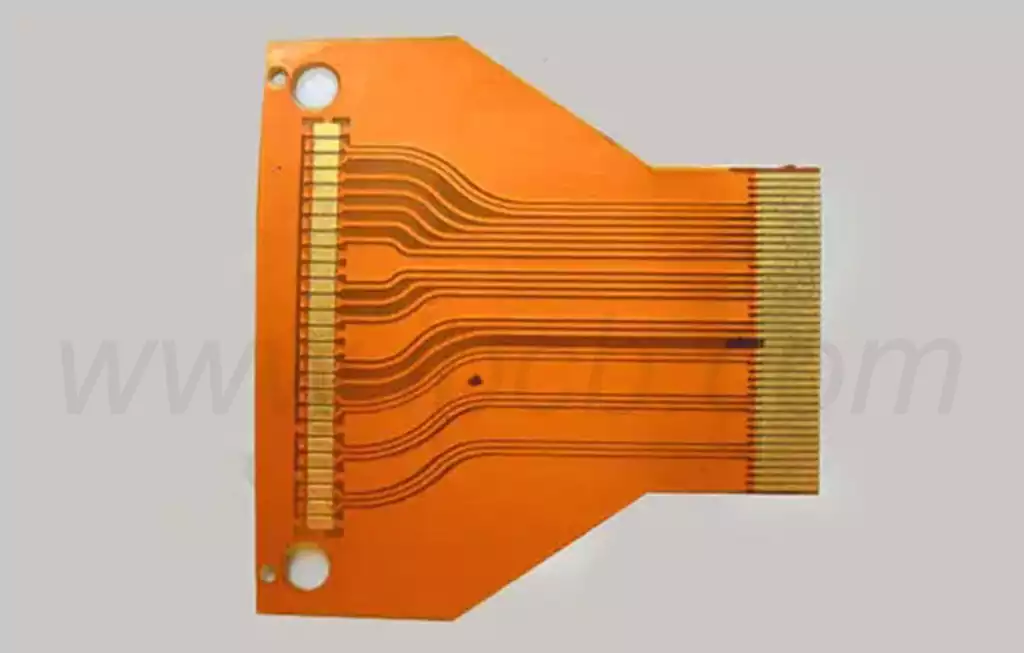
2 layer flex pcb is a printed circuit board designed to be flexible and bendable. Unlike traditional rigid circuit boards, flexible circuit boards are made of thin and flexible materials such as polyimide or polyester film. These materials allow the circuit board to adapt to various shapes and fit into small spaces, making it ideal for applications that require flexibility and space constraints. Also known as flexible circuit board, soft circuit board, flexible circuit board, flexible circuit board, soft board, etc., it is a special printed circuit board. It is characterized by light weight, thin thickness, softness and bendability. It is mainly used in many products such as mobile phones, laptops, PDAs, digital cameras, LCD screens, etc.
Structure of flexible circuit board
Substrate
The substrate of flexible circuit boards is usually a flexible polymer such as polyimide or polyester. Polyimide is favored for its excellent thermal stability and mechanical properties, while polyester is used for cost-sensitive applications.
Conductive layer
The conductive layer in a flexible circuit board is usually made of copper. Copper is selected for its excellent electrical conductivity and flexibility. Depending on the complexity of the circuit design, the copper layer can be single-sided, double-sided or multi-layer.
Adhesive
The adhesive layer is used to bond the conductive copper layer to the flexible substrate. The adhesive must be flexible and durable to maintain the integrity of the flexible pcb under bending and twisting conditions.
Cover Film
The cover film is a protective layer applied to the conductive traces to protect them from environmental factors such as moisture, dust and mechanical damage. The cover film is usually made of the same material as the substrate, such as polyimide.
Type Classification
Single-sided flexible circuit board
Single-sided flexible circuit board has only one conductive layer (mostly metal) attached to a soft insulating layer (substrate), so only one side can be used to place electronic parts or as a conductive contact surface. A layer of insulating material and solder mask (protective film) will be added to the conductive layer for protection. The function is to prevent tinning of places that do not need to be tinned when soldering electronic parts, and to prevent accidental short circuits when the product is used in the future.
Single-layer two-sided exposed flexible circuit board
Single-layer two-sided exposed board also has only one conductive layer, but both sides of the conductive layer can also be conductive contact surfaces or place parts, and both sides have their own solder mask. Because there are not many cases where parts are placed on both sides and a single-layer conductor can meet the wiring requirements, this structure is not common.
Double-sided flexible printed circuit board
Double-layer flexible printed circuit board has two conductive layers, separated by an insulating substrate in the middle, and the outer two layers are covered with an insulating layer for protection/solder resistance, and the conductive layer is exposed at the required position as a connection point or pad. This type of structure does not have a guide hole to allow the two layers to be connected, which limits its use.
Double-layer or multi-layer flexible printed circuit board
Double-layer or multi-layer flexible printed circuit board has two or more conductive layers, each conductive layer is separated by an insulating substrate, and there can be conductive through holes (i.e., vias) at the required position. The outer two layers are covered with an insulating layer for protection/solder resistance, and the conductive layer is exposed at the required position as a connection point or pad. Since there are more than one conductive layer and the layers can be connected by vias, when the line needs to pass through a position blocked by a part or other line, it can be transferred to another conductive layer through the via to avoid the obstruction, solving the wiring difficulties. It is more flexible in application, so it is often used in designs with more complex lines.
Advantages of 2 layer flex pcbs
Flexible pcbs offer several advantages over traditional rigid pcbs:
Flexibility: The most obvious advantage of flexible circuit boards is their flexibility. They can bend and conform to a variety of shapes, allowing for more compact and space-saving designs.
Lightweighting: Flexible circuit boards are typically thinner and lighter than rigid boards, making them ideal for weight-sensitive applications such as aerospace and wearables.
Durability: Despite their flexibility, flexible circuit boards are extremely durable and can withstand repeated bending and folding without damage. This makes them suitable for applications where the board may be subject to constant movement or vibration.
Reduced assembly time: Flexible pcbs can often replace multiple rigid pcbs and connectors, reducing the number of components and simplifying the assembly process. This can result in faster production times and lower assembly costs.
Improved signal integrity: Flexible circuit boards can reduce the need for connectors and cables, which can improve signal integrity by reducing the likelihood of signal loss or interference.
Limitations of Flexible Circuit Boards
While flexible pcbs offer many advantages, they also have some limitations. These include:
Higher initial cost: Due to the need for specialized materials and manufacturing processes, the initial cost of flexible pcbs can be higher than that of rigid pcbs.
Complex design and manufacturing: Designing and manufacturing flexible pcbs may be more complex than rigid pcbs, requiring specialized knowledge and equipment.
Limited load-bearing capacity: Compared with rigid pcbs, flexible pcbs have limited load-bearing capacity, making them unsuitable for applications that require high mechanical strength.
What is the difference between flexible circuit boards and hard pcbs?
About FPC soft boards, which are so-called flexible circuit boards, are actually a type of printed circuit boards, but they are very different from traditional printed circuit boards, so they are called FPC soft boards, and the full name is flexible circuit boards. FPC generally uses PI as the substrate, which is a flexible material that can be bent and flexed at will. FPC soft boards are usually used in places where repeated flexing and the connection of some small components are required, but now it is not just that. At present, smartphones are trying to bendable, which requires the use of FPC soft boards, a key technology. pcb is the so-called printed circuit board, which is usually referred to as a pcb hard board. It is a support body among electronic components and is a very important electronic component. pcb hard boards usually use FR4 as the substrate, also called FR4 circuit boards, which cannot be bent or flexed. pcb hard boards are usually used in places that do not require bending and have relatively strong strength, such as computer motherboards, mobile phone motherboards, etc. In fact, FPC soft boards are not only flexible circuit boards, but also an important design method for connecting to three-dimensional circuit structures. This structure can be combined with other electronic product designs to build a variety of different applications. Therefore, from this point of view, FPC and pcb are very different. FPC soft boards can of course use terminal connection methods for circuit connection, but soft and hard boards can also be used to avoid these connection mechanisms. A single FPC can be configured with many hard boards and connected by layout. This approach reduces the interference of connectors and terminals, and can improve signal quality and product reliability. For pcbs, unless the circuit is made into a three-dimensional form by filling film glue, the circuit board is generally flat. Therefore, to make full use of three-dimensional space, FPC is a good solution. For hard boards, the current common space extension solution is to use slots and interface cards, but FPC can make a similar structure with a transfer design, and it is also more flexible in directional design. With a single FPC connection, two rigid boards can be connected into a set of parallel line systems, or they can be bent at any angle to accommodate different product appearance designs.

Applications of 2 layer flex pcbs
- Consumer electronics: Flexible pcbs are commonly used in smartphones, tablets, laptops, and wearable devices, where space is limited and flexibility is required.
- Medical devices: Flexible circuit boards are used in medical devices such as hearing aids, pacemakers, and implantable devices, where their flexibility and compact size are essential.
- Automotive: In the automotive industry, flexible pcbs are used in applications such as dashboard displays, sensors, and control modules, where they must be able to withstand harsh environments and continuous vibrations.
- Aerospace: Flexible pcbs are used in aerospace applications such as satellites, aircraft, and missiles, where their lightweight and compact size are critical.
- Industrial: Flexible circuit boards are used in industrial applications such as robotics, automation, and process control, where their flexibility and durability are important.
Can flexible circuit boards be used in high-temperature applications?
Yes, flexible circuit boards can be used in high-temperature applications. Polyimide is the most commonly used substrate for flexible circuit boards. It has a high glass transition temperature and can withstand temperatures up to 300°C. However, the maximum operating temperature of flexible circuit boards also depends on the temperature grade of the materials used in components and assembly.
What are the components of FPC processing costs?
Although the printed circuit board industry has some common basic processes, the most important thing is to determine different production processes and equipment based on the thickness and material of the substrate, the precision requirements of line width and line spacing, the design structure and production scale, and other special requirements specified by the customer, resulting in a large difference in the cost of making FPC. FPC is a highly customized product, and there are many components of the cost of flexible circuit boards. For novice purchasers of electronic manufacturers, it is necessary to understand the components of the cost of 2-layer flexible circuit boards before making flexible circuit board samples.
The production process of FPC flexible circuit boards is relatively complicated, usually with more than 40 processes such as inner layer production, exposure, lamination, drilling, electroplating, etc. Taking FPC as an example, it usually includes exposure, development, etching, copper plating, film stripping and other processes. Although FPC has a strong customization feature, these most basic processes are necessary, but there will be differences in specific parameters. In fact, each process of FPC is already relatively mature, so cost control ability has become the most critical factor in the profitability difference of FPC flexible circuit board manufacturers. Cost control is reflected in all aspects of the operation of flexible circuit board manufacturers, which directly depends on the company’s management level and needs to start from the details.
In the cost structure of FPC flexible circuit boards, direct material costs usually account for about 60%, direct labor costs usually account for about 15%, and manufacturing cost costs usually account for about 25%.
With the continuous advancement of technology and the growing demand for smaller, lighter and more flexible electronic products, the use of 2 layer flex pcb is expected to increase. By understanding the advantages, applications, design considerations and manufacturing processes of flexible circuit boards, engineers and manufacturers can create innovative and reliable products that meet the changing needs of customers.