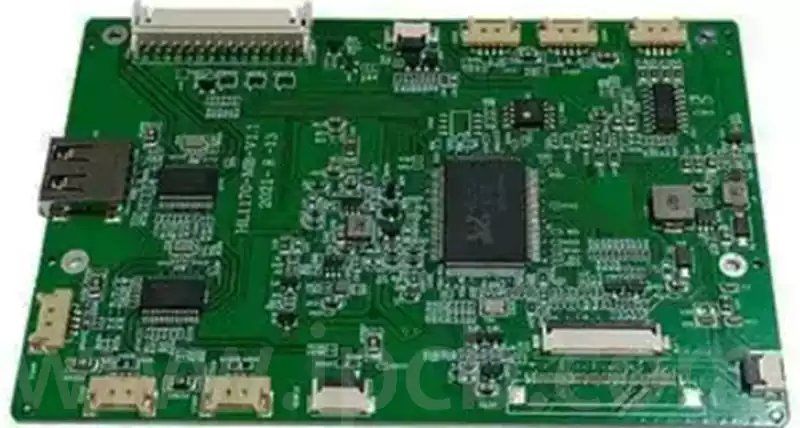
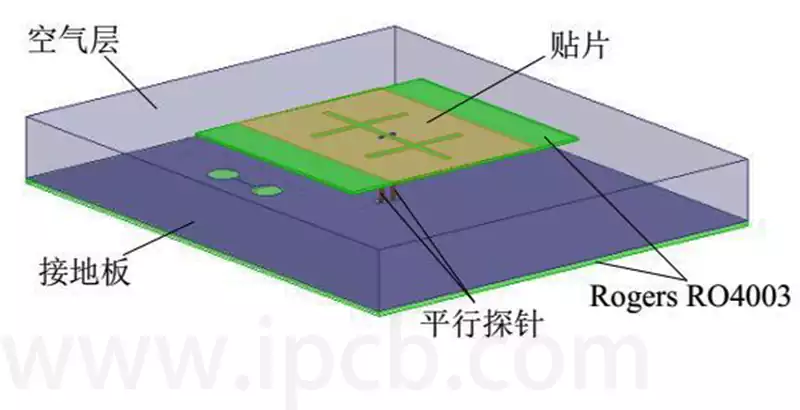
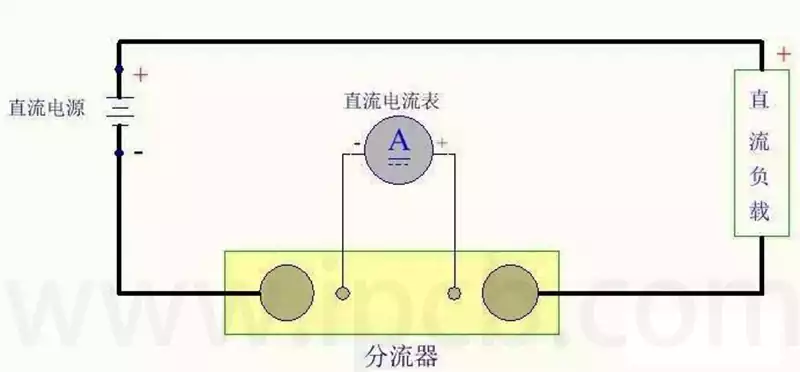
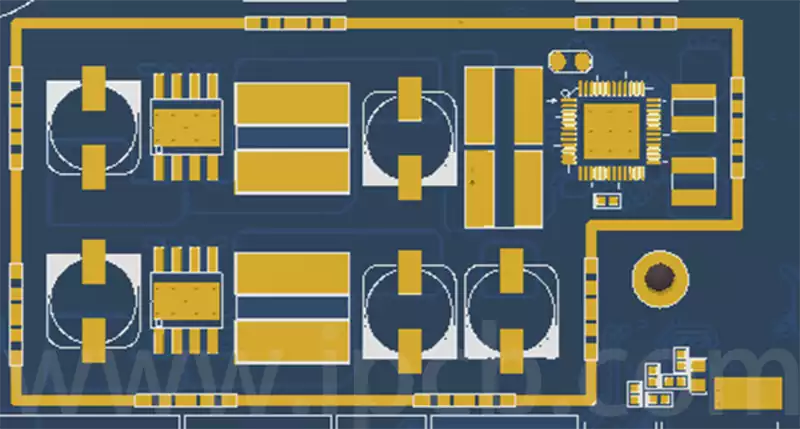
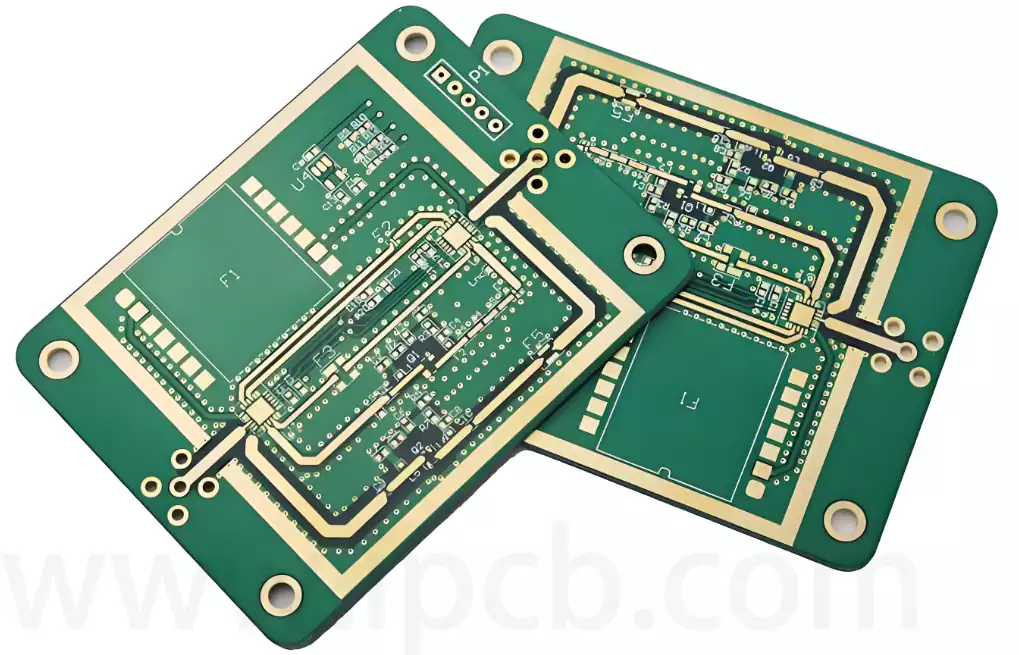
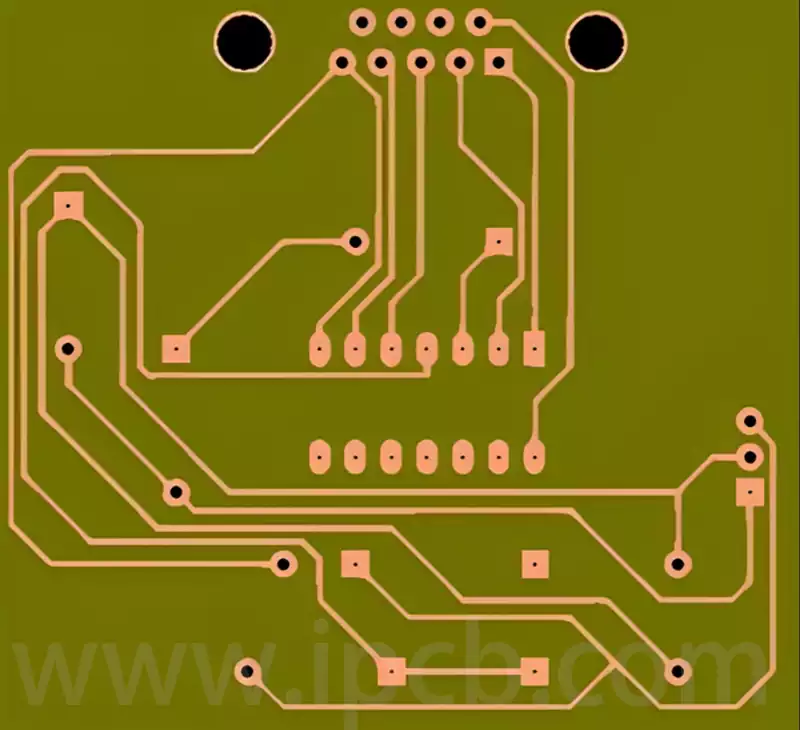
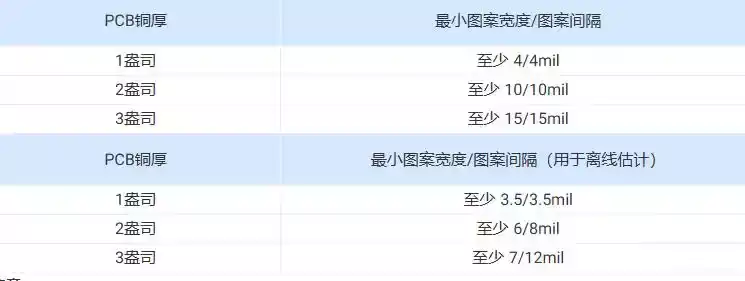
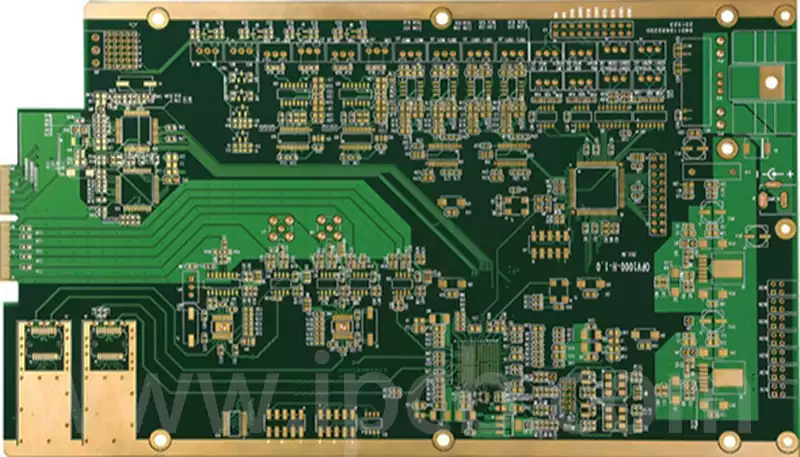
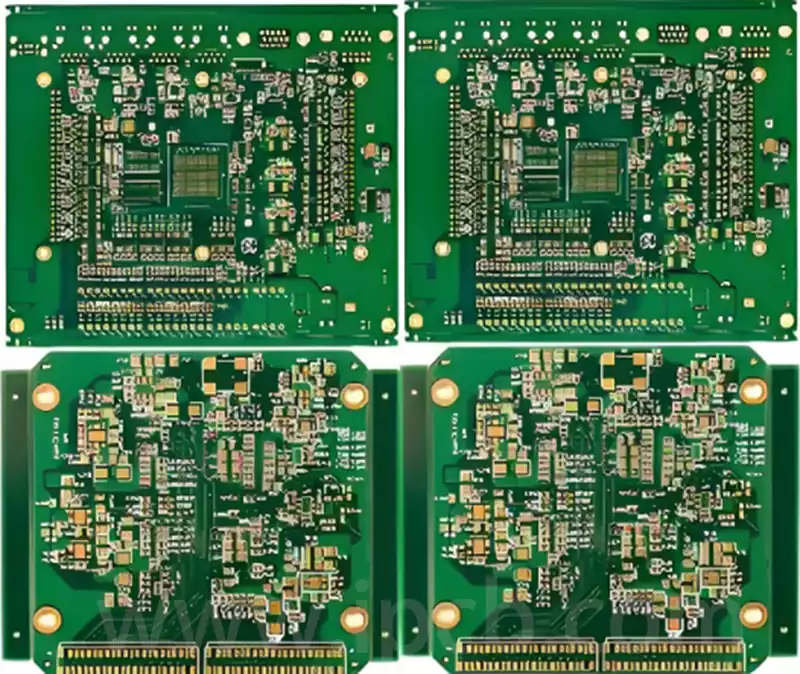
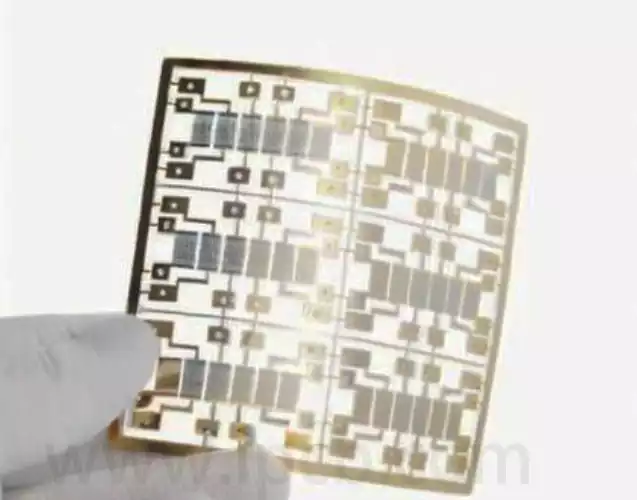
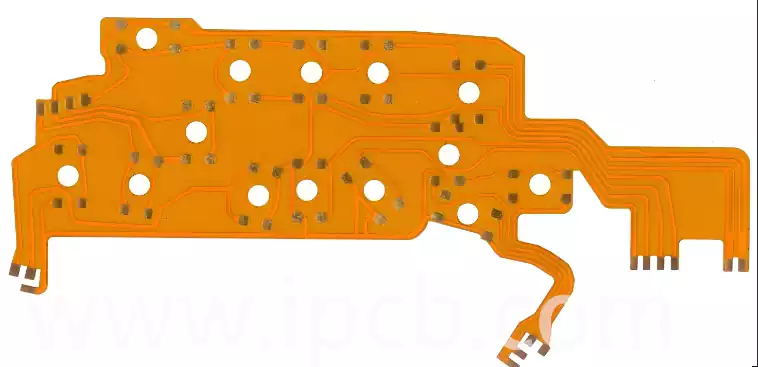
Technical applications of eutectic solder
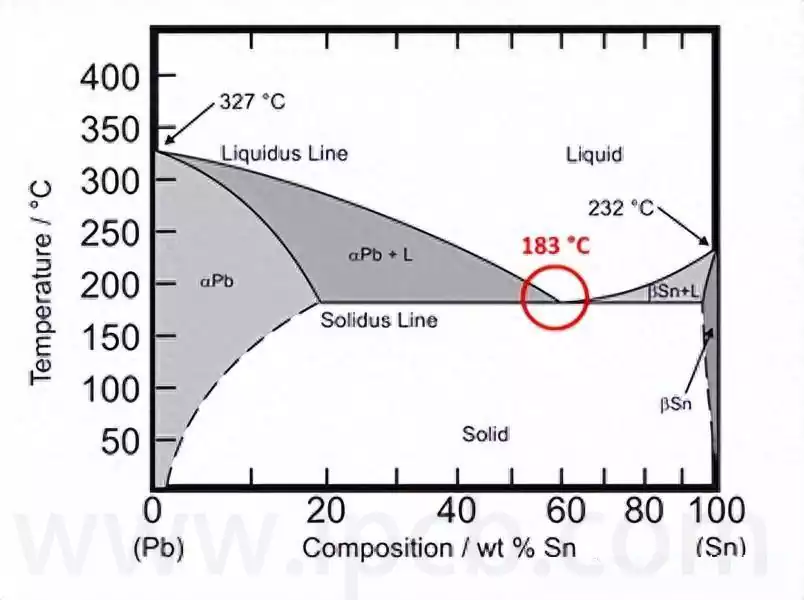
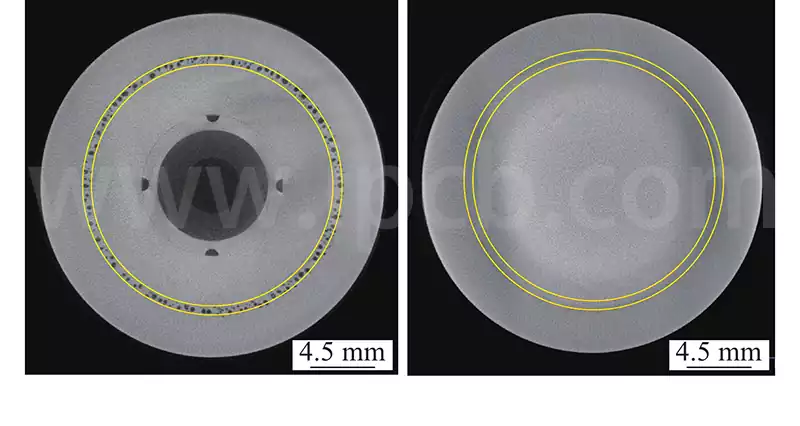
Eutectic soldering, also known as low melting point alloy soldering, is a specific soldering technique. The process involves the removal of unstable oxide layers at the interface between the chip and the gold-plated base by gentle friction at specific temperatures and pressures, which causes the contacting surfaces to melt and form a liquid phase. Subsequently, […]