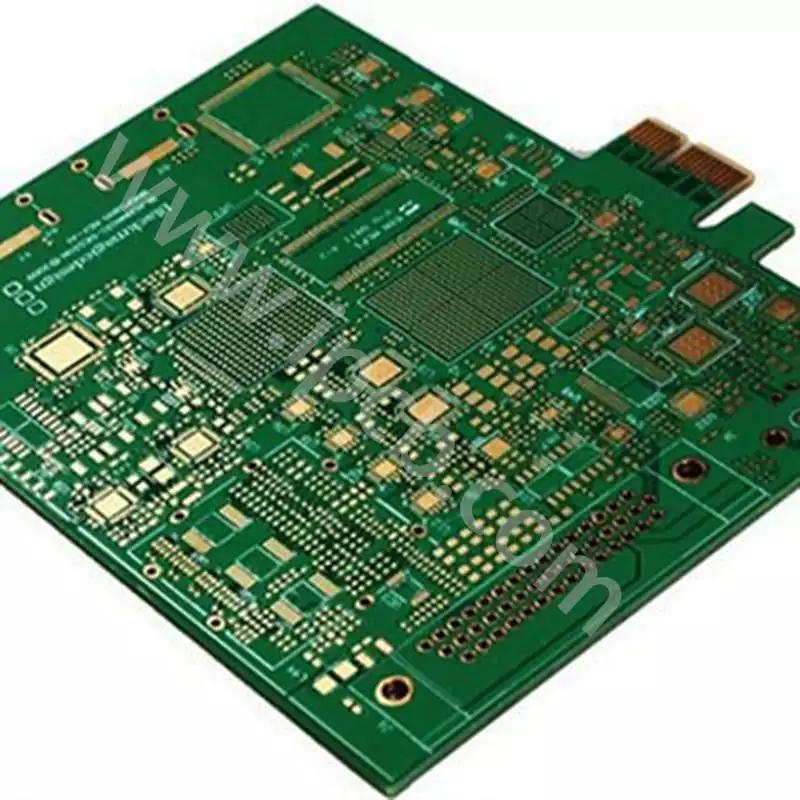
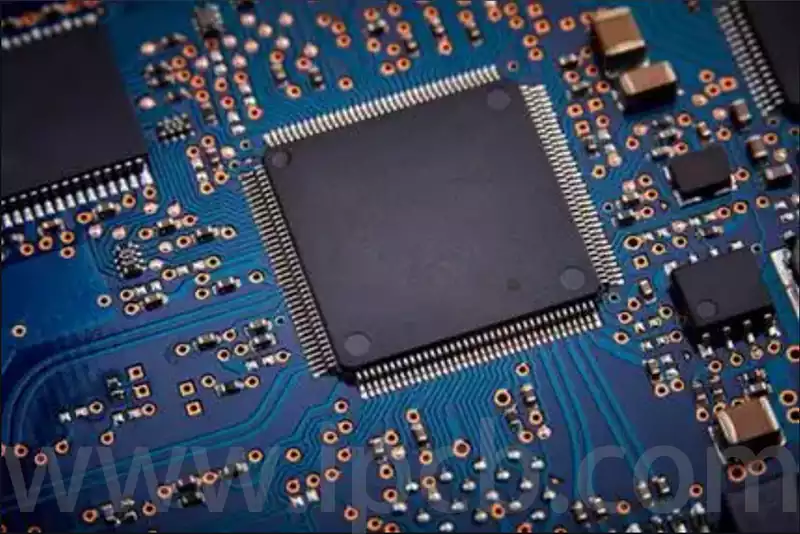
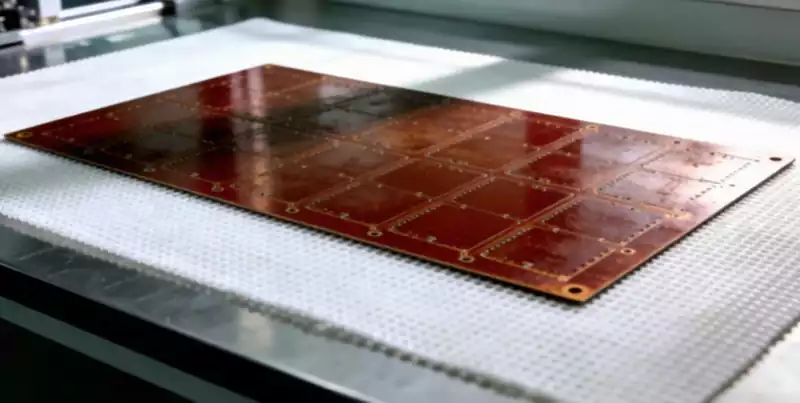
Burn-in board is a special kind of circuit board, which is a high-quality circuit board after special processing, mainly used for aging tests. This kind of board has special sockets for fixing ICs in it. Aging boards are mainly used for aging tests of electronic components, including high temperature, high humidity, double 85 test, and other online tests to ensure their stable and reliable performance. During the testing process, the aging board will be exposed to high temperatures, high humidity, and other harsh environments, so it is necessary to use special materials that can withstand these conditions. Depending on the temperature requirements, special versions of flame retardant or FR4 materials (high Tg FR4) can be used, or even high-temperature materials such as polyimide. Aging tests ensure that electronic components have been adequately tested for thermal stability and reliability before they are used, thus prolonging their service life and improving the reliability of the product.
Burn in board is a special kind of circuit board that is mainly used for the aging test of electronic products. To meet the aging test requirements, aging boards need to have the following characteristics:
High-temperature performance: In the aging test process, electronic components will be exposed to high temperatures, so the aging board needs to be able to withstand high-temperature environments without deformation, discoloration, or softening.
Corrosion resistance: In some cases, an aging test will be used in corrosive gases or liquids, so the aging board needs to have corrosion resistance to prevent corrosion damage.
Good electrical properties: the aging board needs to have good electrical properties, including insulation resistance, electrical conductivity signal transmission ability, etc., to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the test results.
Stable structure: the aging board needs to have a stable structure to ensure that in the process of multiple uses will not occur deformation or fracture and other phenomena.
Easy to clean and maintain: The aging board needs to be easy to clean and maintain to ensure its long-term performance and service life.
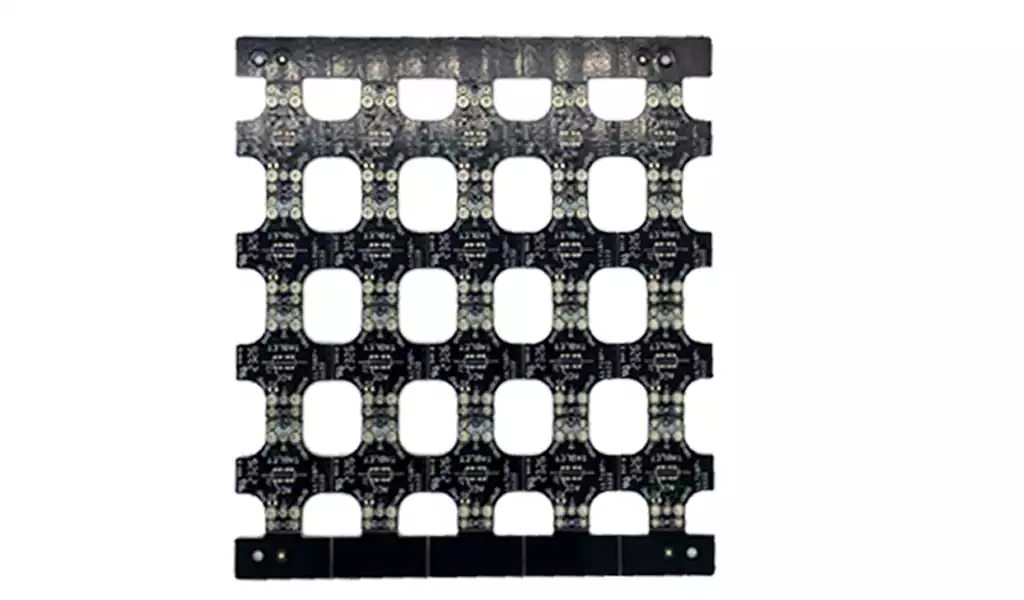
The test temperature range of the high-temperature the board is 105℃ to 150℃, which is determined by its application environment and test requirements. The performance of electronic components may be affected under high-temperature environments, so a high-temperature aging test is needed to simulate the high-temperature environment in actual use to evaluate their stability and reliability under high temperatures.
The following aspects need to be considered when selecting the test temperature range of high-temperature aging boards:
The maximum working temperature of electronic components: Different electronic components have different maximum working temperatures, so it is necessary to choose a reasonable test temperature range to simulate the high-temperature environment in actual use. If the test temperature is lower than the maximum working temperature of the electronic components, then the results of the aging test may be inaccurate and unable to reflect the true performance of electronic components at high temperatures.
Testing time and heating rate: The longer the testing time and the faster the heating rate of the high-temperature aging board, the higher the requirements for the material. Therefore, when selecting the test temperature range, the influence of test time and heating rate need to be considered to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the test results.
Test purpose and requirements: Different test purposes and requirements require the selection of different test temperature ranges. For example, for some specific electronic components or applications, higher test temperatures may be required to simulate extreme environments in actual use.
IPCB is a BIB (Burn-In Board) manufacturer, provides professional aging test boards.