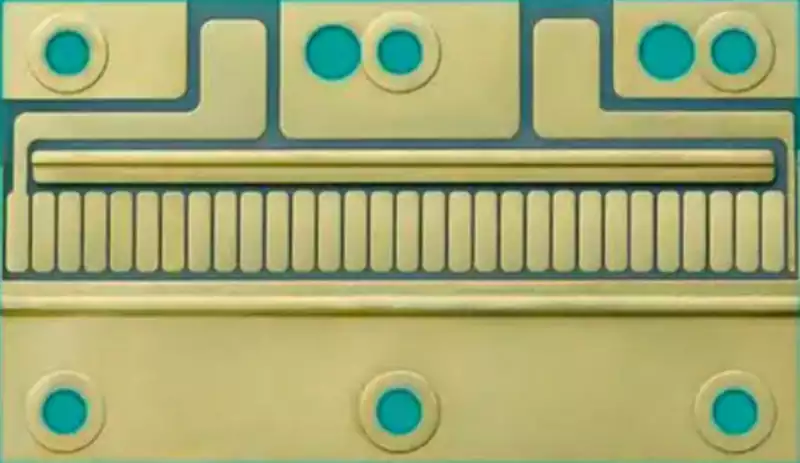
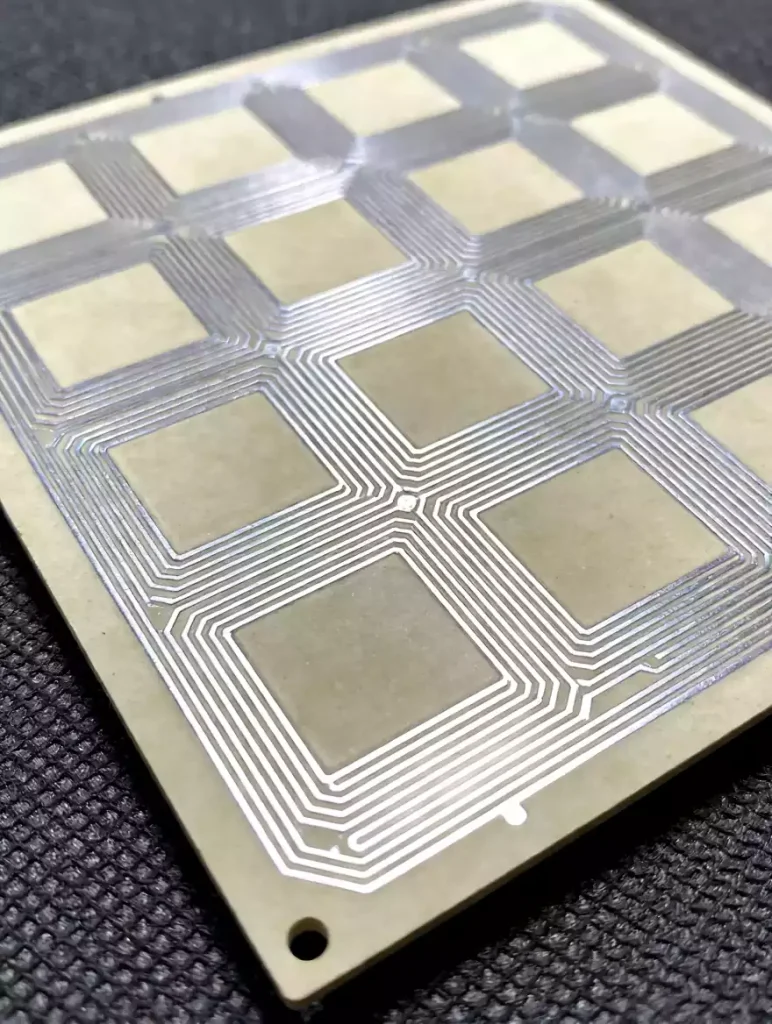
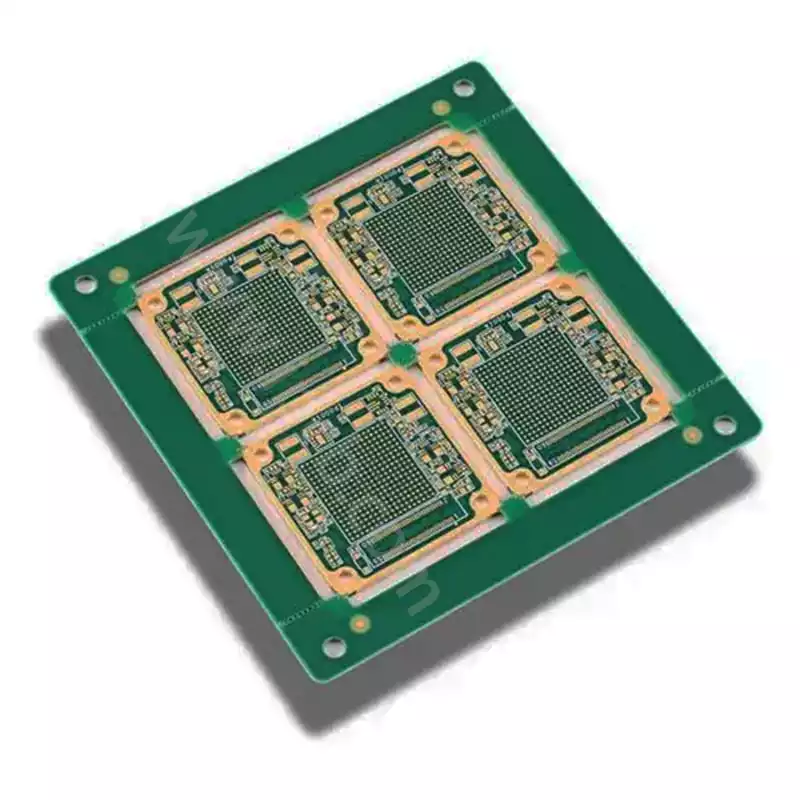
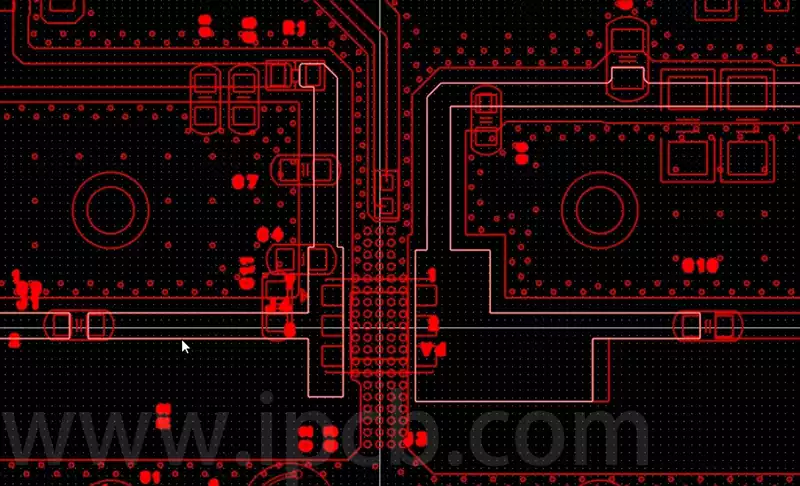
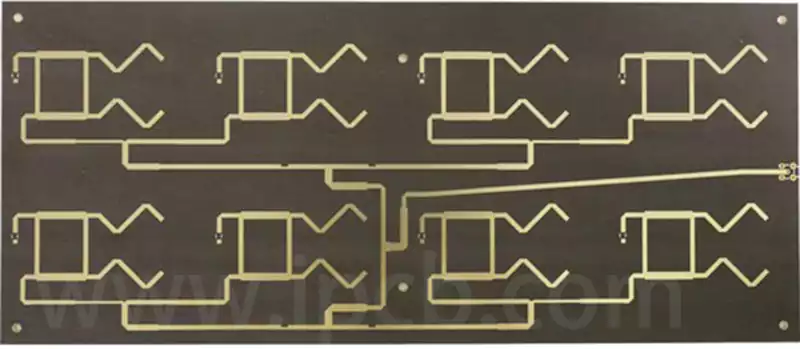
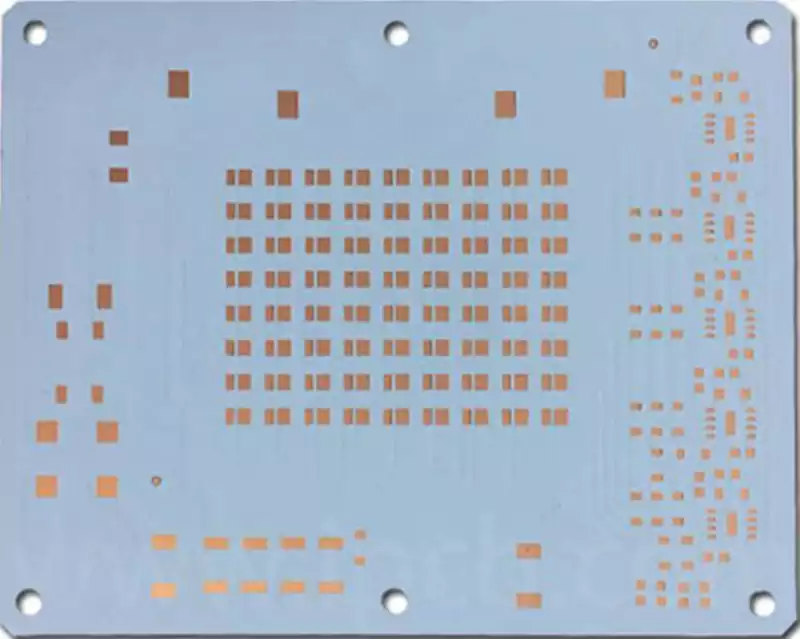
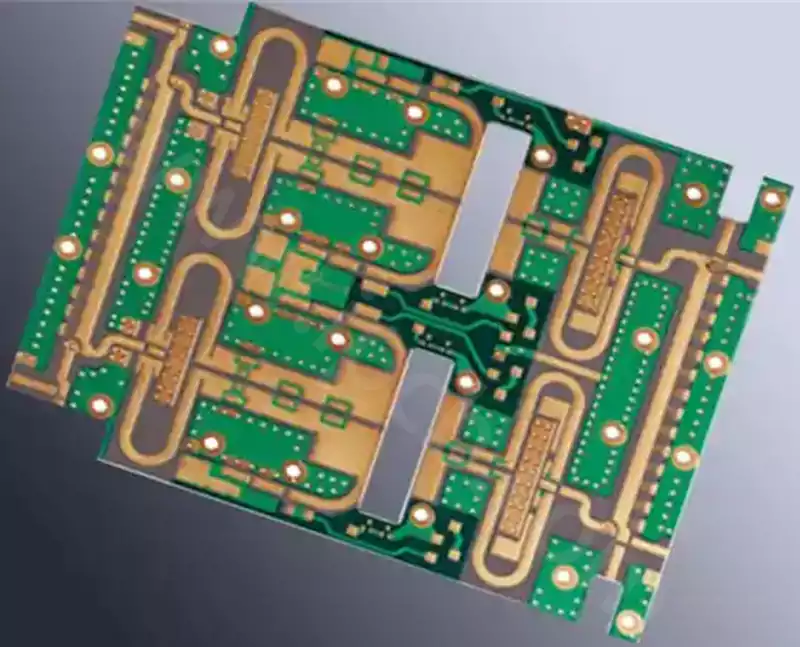
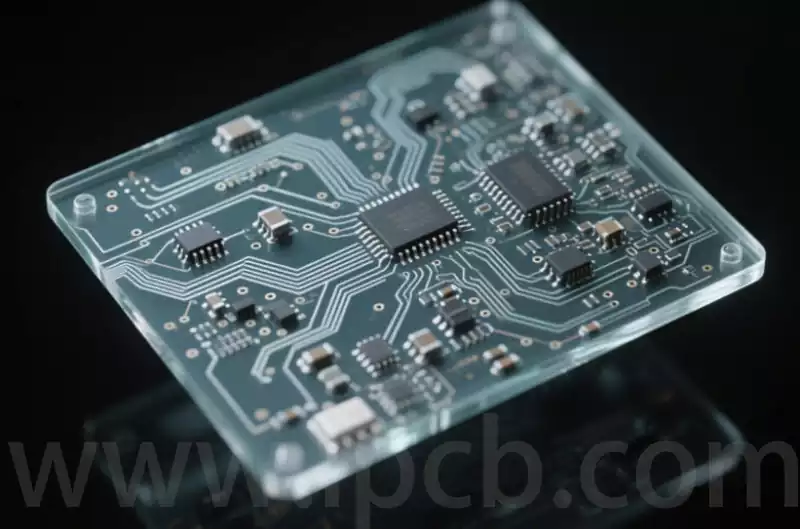
Aluminium nitride ceramic circuit boards empower laser diode applications
Behind the faint light pulses of laser diodes lies an uncompromising demand for substrate material. From the precise detection of autonomous driving lidar to the high-speed transmission of 800G optical modules, each stable emission relies on ceramic circuit board substrates for efficient thermal dissipation and structural precision. Among numerous ceramic substrates, aluminium nitride (AlN) stands […]