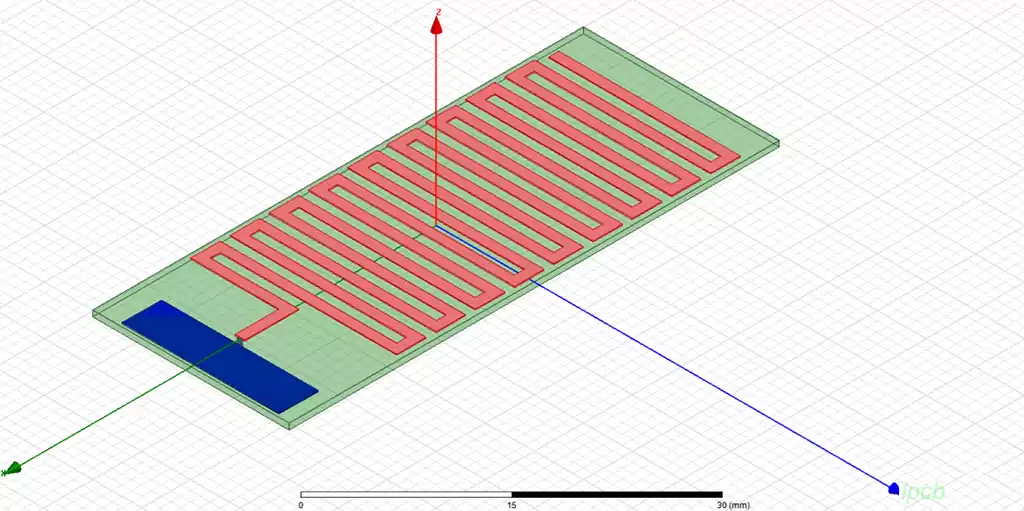
What is a PCB antenna? As the name suggests, it is a PCB printed on an alignment, which can be drawn as a straight line alignment, reversed F-shaped alignment, snake or circular alignment, etc., the length of a quarter wavelength can basically form an antenna to radiate electrical signals out or receive signals.
Design elements
- Frequency: The frequency of PCB antenna determines the range of signals it can send and receive. Frequency is related to the physical size of the antenna, and lower frequencies require longer antenna lengths.
- Gain: The gain of it determines the size of its radiated power. The higher the gain, the farther the antenna radiates.
- Directionality: The directionality of it determines the direction range of its radiated and received signals. The stronger the directionality, the better the signal transmission effect of the antenna in a particular direction.
- Impedance matching: Impedance matching is required between PCB antenna and radio frequency transmitter or receiver to ensure maximum efficiency of signal transmission.
Advantages:
- Compact size: it can be precisely sized according to the design requirements, so that it occupies less space in the equipment. This is very important for the modern trend of smaller and smaller electronic devices.
- Punching positioning:it is usually positioned by punching holes in the printed circuit board.This design allows the antenna to be tightly integrated with other circuit components, improving the reliability and stability of the overall system.
- Adaptable: it has a high degree of design flexibility and can be customized for different applications. It can be adjusted according to frequency, antenna type (e.g. patch antenna, spiral antenna, etc.) and antenna shape.
- Good performance: PCB antennas usually have good performance, such as high gain, low distortion, stable impedance matching and so on. These features ensure that the antenna is effective in transmitting and receiving signals in wireless communication.
- Cost-effective: Since it can be manufactured at the same time as other circuit components, they can be mass-produced in the manufacturing process, thus reducing costs. In addition, it is relatively simple to manufacture and install, which can increase productivity.
Disadvantages:
The performance of the antenna is affected by factors such as PCB fabrication process and line length.
The higher matching transmitter cost of PCB antennas.
Trying to change its performance or shape is very difficult.
PCB antennas and rod antennas are two common antenna types that differ in shape, performance, and application.
PCB antennas are antennas on a printed circuit board, usually made of metal foil. They can be designed in various shapes and sizes to suit different application scenarios. PCB antennas are typically used in small devices such as smartphones, wireless sensors, and IoT devices. They can be designed into very small sizes to fit into the restricted space of these devices. In contrast, rod antennas are long, thin antennas usually made of metal rods. They are typically used for large devices such as TV antennas, vehicle antennas, and base station antennas. The length and diameter of rod antennas can be adjusted as needed to accommodate different frequencies and application scenarios.
Performance:PCB antennas usually have lower gain and smaller bandwidth, but they can be designed with multiple frequency bands and polarization directions. Rod antennas typically have higher gain and larger bandwidth, but they can usually only be designed with a single band and polarization direction.
Applications:PCB antennas are typically used for small devices and low-power applications such as smart homes, smart wearables, and IoT devices. Rod antennas are usually used for large devices and high power applications, such as TV, radio communication and radar.
As an integral part of modern electronic devices, PCB antennas play an important role in wireless communications due to their compact size, adaptability, and cost-effectiveness. Despite the limitations of fabrication process and performance tuning, its wide application in small devices and low power applications cannot be ignored.