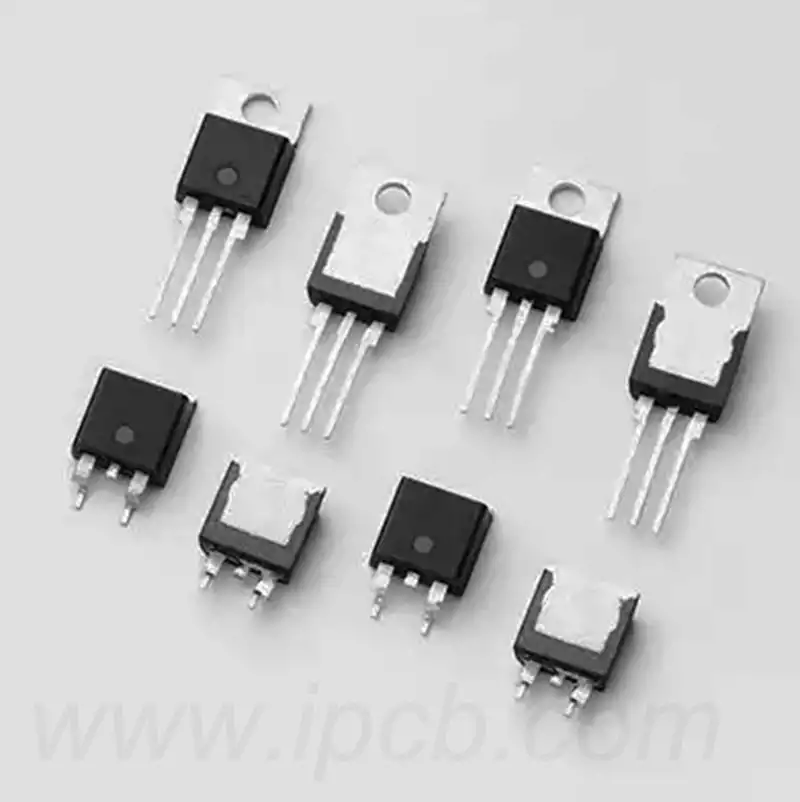
What is a transistor? It is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electronic signals and electricity, which consists of semiconductor material that usually consists of at least three pins for connecting to external circuits, and is an important electronic component in PCBA boards. They are mainly divided into two categories: bipolar junction transistors and field effect transistors.
Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)
BJT, also known as semiconductor triode. It is due to the fact that it is carried out by using majority and minority carriers, it is the first type of it to be mass-produced and is a combination of two junction diodes and consists of a thin film of a p-type semiconductor sandwiched between two n-type semiconductors,or a thin layer of an n-type semiconductor sandwiched between two p-type semiconductors. The structure produces two p-n junctions: a base, an emitter junction, and a collector junction, separated by a thin semiconductor region in the middle base region.
The BJT has three terminals corresponding to the three semiconductor layers (emitter, base and collector). They are useful in amplifiers because the currents at the emitter and collector can be controlled by the relatively small base current. In an n-p-n transistor operating in the active region, the emitter, base junction is forward biased (electrons and holes are complexed at the junction) and electrons are injected into the base region. Because of the narrow base, most of these electrons will diffuse into the reverse-biased base and collector and be swept into the collector; perhaps one percent of the electrons will recombine in the base, which is the dominant mechanism in the base current. The number of electrons entering the collector is controlled by controlling the number of electrons that can leave the base. The collector current is about β (co-emitter current gain) of the base current. It is typically greater than 100 for small-signal transistors and can be smaller in transistors designed for high-power applications.
Unlike field effect transistors, BJTs are low input impedance devices. In addition, as the base and emitter voltages (VBE) increase, the base and emitter currents and collector and emitter currents (ICE) increase exponentially according to the Shockley diode model and the Ebers-Moll model. Due to this exponential relationship, BJTs have higher transconductance of FETs.
BJT can conduct by exposure to light because the absorption of photons in the base region produces a photocurrent as the base current; the collector current is about β times the photocurrent. Devices designed for this purpose have transparent windows in the package and are called phototransistors.
Field effect transistors are primarily used to conduct electrons (in n-channel FETs) or holes (p-channel FETs). The four terminals of the FET are called source, gate, drain and body (substrate). In most FETs, the body is connected to the source inside the package.
There are two types of BJTs, NPN and PNP transistors.
An NPN transistor is a combination of two N-type materials and one P-type material.The P-region is sandwiched between the N-regions. The three terminals, collector, base and emitter, rise from the N-region, P-region and N-region respectively.
The majority carriers are electrons and the minority carriers are holes. Applying current IB at the base terminal allows current IC to go from the collector to the emitter. The current is proportional to the base current. And the total emitter current IE is the sum of the base current Ib and the collector current IC.
The symbols of an NPN transistor also indicate the direction of the current. The small arrow pointing outward from the emitter indicates the direction of current outward from the emitter.
An NPN transistor is switched by applying a positive base-emitter voltage VBE, which has a high switching speed because most of the carriers are electrons.
A PNP transistor consists of a combination of two P layers and an N layer. The thin N layer is sandwiched between the two thick P layers. The middle N layer is called the base and the two surrounding layers are called the collector and emitter.
Most of the carriers are holes and a few carriers are electrons.
Reverse biasing the collector-emitter junction and forward biasing the base-emitter junction puts it into the conduction mode where the output current is proportional to the base current.
The PNP transistor conducts when a negative voltage VBE is applied to the base region and turns off when a positive voltage is applied to the base region.
Since most of the carriers are holes, the recovery time of a PNP transistor is relatively high, and hence its switching speed is lower than that of an NPN transistor.
In the symbol for a PNP transistor, the arrows pointing inward indicate the direction of current flow inside the emitter to the base and collector. Thus, the total current IC is the emitter current minus the base current.
The role of transistors in PCBA mainly includes the design and fabrication of logic gate circuits.
Transistor is an electronic component made of semiconductor material which has a wide range of applications and can be used in a variety of circuits. In PCBA boards, they are mainly used in the design and fabrication of logic gate circuits. Logic gate circuits are the basic components in digital circuits and are used to implement various logic functions such as and, or, and not. They are used to realize logic operations by controlling the on/off or change of current to perform complex logic functions on PCBA boards.
In addition, transistors have applications in amplification circuits, switching circuits, signal processing circuits, and so on. For example, in amplification circuits, it can amplify weak signals into electrical signals with larger amplitude values, increasing the strength of the signal for subsequent processing or transmission. In switching circuits,it can be used as switches to realize the switching function of the circuit by controlling the on-off of the current. In signal processing circuits, it can be used for filtering, modulation, and other operations to process signals to meet specific needs.
Common and critical electronic components in the design and manufacture of electronic circuits include diodes, Recognizing these transistor types accurately is a basic and important technical skill in the PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) process.