Flexible PCB assembly refers to circuit boards manufactured using flexible substrates, offering superior bendability and adaptability compared to traditional rigid PCBs. Flexible PCB assembly enables higher-density routing, saving space and making it suitable for devices with complex geometries.
Flexible PCB assembly possesses the following characteristics and advantages:
Flexibility and Bendability
Flexible PCB assembly can be freely bent, coiled, or folded to accommodate intricate spatial layouts, enabling flexible assembly within three-dimensional spaces. This satisfies the demand for miniaturisation and lightweight design in electronic products.
Thinness and Lightweight
Its slim profile and light weight contribute to reducing overall product mass, enhancing portability, and making it suitable for volume- and weight-sensitive devices such as smartphones and wearable technology.
High Wiring Density
Enables dense placement of precision components within confined spaces, enhancing circuit integration to meet high-density assembly requirements in electronics.
High Reliability
Superior thermal dissipation and solderability, coupled with simplified assembly processes, reduce solder joints and connectors. This lowers failure rates while improving resistance to vibration and impact.
Applications of Flexible PCB Assembly in Smartphones
Foldable and Curved Display Technologies:
FPC flexible circuit boards constitute the pivotal technology enabling foldable smartphones to achieve screen folding and unfolding, delivering expanded display areas and enhanced user experiences.
In curved-screen smartphones, FPCs integrate with curved glass to facilitate arched screen designs, thereby elevating aesthetic appeal and tactile comfort.
Internal Connections and Module Integration: Flexible PCB assembly is extensively employed within mobile phones for internal wiring, ensuring flexible connections between hardware components to enhance device stability and reliability. FPC flexible circuit boards can be integrated into multiple hardware elements including cameras, displays, touchscreens, batteries, antennas, fingerprint modules, and buttons. FPCs also feature high wiring density, lightweight construction, bendability, and suitability for three-dimensional assembly. Flexible Printed Circuits (FPC) constitute a general term for pliable printed circuit boards, formed by laminating flexible copper-clad laminate (FCCL) and flexible insulating layers using adhesive. FPCs possess soft, bendable, and foldable properties, making them highly suitable for installation and wiring within confined and irregular spaces.
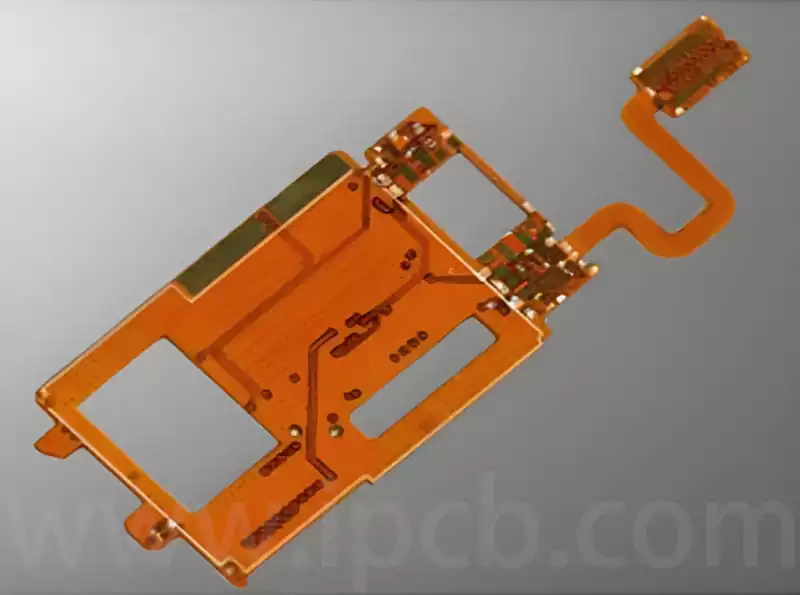
Applications of Flexible PCB Assembly in Smart Homes
Smart Lighting Systems: Flexible PCB assembly can be utilised in manufacturing light strips for smart lighting fixtures. When combined with LED bulbs, they enable vibrant lighting effects and can be bent and extended as required, facilitating installation and arrangement.
Smart Door Locks: In the circuit board manufacturing of smart door locks, the use of flexible PCB assembly facilitates adaptable designs to accommodate varying shapes and dimensions, enhancing both the intelligence and security of the locks.
Control Centre Mainboards: Flexible PCB assembly is also employed in manufacturing mainboards for smart home control centres. This enables compact mainboard designs and flexible layouts, facilitating user control and management of smart home devices. FPCs are extensively utilised in battery connection and power distribution systems for smart home devices. For instance, micro-connectors are soldered onto FPCs via SMT assembly to achieve efficient connections between battery packs and mainboards. Furthermore, the flexible design of FPCs prevents connection issues caused by device vibration.
Unique Process Requirements for Flexible PCB Assembly
Material Compatibility: The substrate of flexible printed circuits (FPC) is typically polyimide (PI) or polyester (PET), materials that differ significantly from those used in traditional rigid PCBs. During surface mount assembly, it is essential to ensure that electronic components, solder paste, adhesives, and other materials exhibit excellent compatibility with the FPC substrate. When procuring SMT materials, Shenzhen Jiechuang Electronics rigorously selects components and auxiliary materials with high compatibility for flexible circuit boards. Regarding solder paste selection, its wettability and adhesion on flexible substrates are considered to prevent soldering defects or circuit board damage caused by material incompatibility.
Precise Positioning and Placement: The flexible nature of FPCs, which can bend and deform easily, presents challenges for positioning and placement during SMT processing. To ensure electronic components are accurately placed on flexible circuit boards, high-precision positioning equipment and processes are required. Shenzhen Jiechuang Electronics employs placement machines equipped with advanced vision recognition systems. These systems monitor the position and deformation of flexible circuit boards in real-time during placement, automatically adjusting placement parameters based on monitoring results to achieve precise component placement. Prior to placement, flexible circuit boards are secured and supported to minimise deformation during processing.
Stress Control: As stress arises during the bending and folding of flexible circuit boards, and electronic components become sensitive to mechanical stress after soldering, stringent stress control is essential during the placement process. Shenzhen Jiechuang Electronics optimises component layout in its process design, endeavouring to position stress-sensitive components in areas of the flexible circuit board less prone to deformation. In soldering processes, low-temperature soldering or materials with thermal expansion coefficients similar to the flexible PCB are employed to minimise thermal stress-induced solder joint cracking or component damage.
Specialised Process Challenges for Flexible PCB Assembly
Soldering Process Challenges: Flexible PCBs exhibit relatively poor heat dissipation, making them prone to localised overheating during soldering. This can lead to PCB deformation and solder joint defects such as cold solder joints. For miniaturised, high-density flexible PCBA assemblies, the narrow pin spacing between components further complicates soldering. Shenzhen Jiechuang Electronics addresses this by optimising reflow soldering temperature profiles. Employing multi-zone heating with gradual temperature ramping ensures even heat distribution, minimising localised overheating. Concurrently, high-precision soldering equipment and advanced techniques—such as laser soldering and selective soldering—enhance joint integrity to overcome these process challenges.
Inspection and Quality Control: Traditional inspection methods like AOI (Automated Optical Inspection) exhibit limitations when examining flexible PCB Assembly. Due to the flexible circuit board’s bendability and surface flatness issues, AOI may fail to accurately detect all soldering defects and component placement problems. Shenzhen Jiechuang Electronics has introduced X-ray inspection technology, which penetrates flexible circuit boards to assess internal solder joint quality, thereby compensating for AOI’s shortcomings. Concurrently, a rigorous quality control system has been established, with stringent oversight at every stage—from raw material inspection and production process monitoring to finished product testing—ensuring the quality of flexible PCB Assembly.
Process Protection: Flexible circuit boards are susceptible to mechanical damage during processing, such as scratches and creases. Such damage may compromise the board’s electrical performance and reliability. Shenzhen Jiechuang Electronics implements a series of protective measures during processing, including the use of soft tooling fixtures and protective mats on workbenches, to prevent contact with hard surfaces. During handling and storage, flexible PCBA are also properly packaged and shielded to ensure their integrity throughout the entire manufacturing process.
Flexible PCB Assembly, with its unique flexibility, slim profile, high density, and exceptional reliability, has become an indispensable key technology in sectors such as smartphones and smart home devices. Despite manufacturing challenges, flexible PCBA continues to overcome technical bottlenecks, driving the evolution of electronic products towards smaller, lighter, and smarter designs. Undoubtedly, flexible PCBA will continue to play a central role in electronic innovation, unlocking further possibilities.