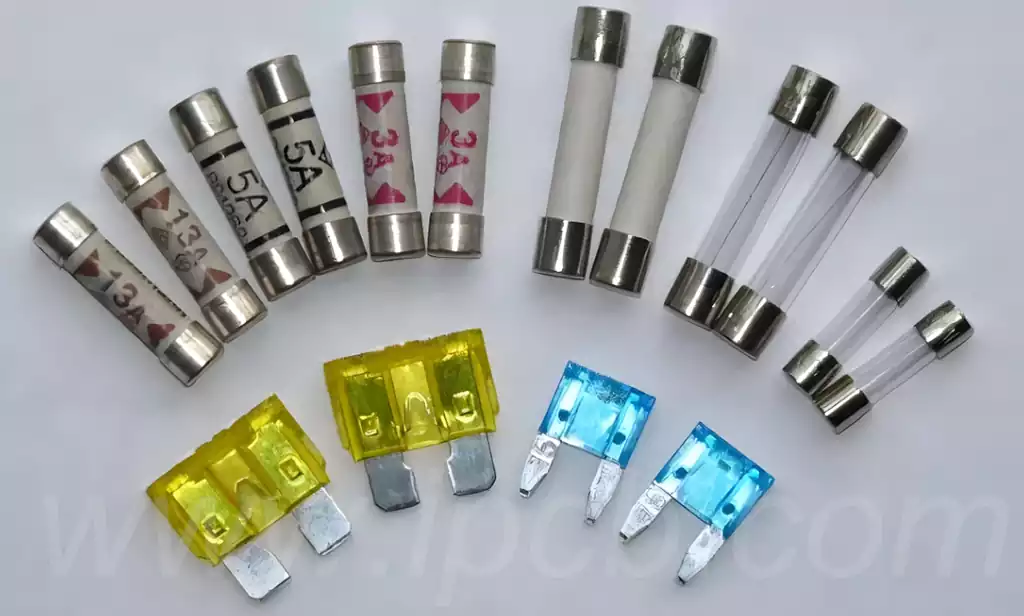
Circuit board fuse serves a vital protective role in electronic equipment. As an overcurrent protection device,fuse in circuit board can effectively prevent damage to circuits caused by overloads or short circuits. Printed circuit board fuses are available in a variety of shapes, including bar wire, sheet (bare), glass tube, ceramic tube, plastic sheet with metal tabs (as is common for automotive fuses), and cylinder, to suit different circuit board designs and applications.
When a circuit encounters a malfunction or abnormal condition, the current may be abnormally high, and this abnormal current level may not only damage critical components in the circuit, but may also lead to serious consequences such as circuit burnout or even fire. However, if the circuit is pre-installed with a fuse, especially one designed for circuit boards, when the current rises abnormally to a certain threshold, along with an increase in temperature, the fuse will quickly blow, effectively cutting off the current, protecting the circuit from further damage and ensuring the safe operation of the circuit.
Circuit board fuse is usually composed of three key parts:
One is the melt part, which is the core component of the fuse, when the current is abnormal, it is this part of the melt, thus cutting off the current. For the same type of fuse with the same specifications, the fuse should be made of the same material, have the same geometry, the smallest possible resistance value, and most importantly, their melting characteristics must be the same. In circuit board fuse, the melt is often made of lead-antimony alloy and other materials to adapt to the working environment and requirements of the circuit board.
Second, the electrode part, usually two, they are the important bridge between the melt and the circuit connection. The electrode part must have good electrical conductivity to ensure that the current can pass through smoothly, and at the same time, it should not produce obvious mounting contact resistance, so as not to affect the normal operation of the circuit.
Third, the bracket part, the fuse (especially circuit board fuse) of the melt is usually slim and soft, need bracket to fix, make it a rigid whole, easy to install and use. The bracket part must have good mechanical strength, insulation, heat resistance and flame retardancy to ensure that no breakage, deformation, burning or short-circuiting will occur during the use of the phenomenon, so as to ensure the stability and reliability of the circuit board fuse.
Fuse in circuit board can be classified according to different protection mechanisms and uses as follows:
From the protection form, the fuse in circuit board is mainly divided into two categories of overcurrent protection and thermal protection. Among them, for overcurrent protection is the conventional fuse, also known as current-limiting fuse; and for thermal protection is known as thermal fuse. Thermal fuse in circuit board can be subdivided into low-melting-point alloy type, temperature-sensitive trigger type and memory alloy type according to different design principles. They are mainly used to prevent electrical equipment from being damaged due to high temperature, such as hairdryers and irons, etc. The working mechanism of this type of fuse does not depend on the size of the operating current of the circuit.
In terms of application, printed circuit board fuses can be classified into electric fuses, machine tool fuses, electrical instrumentation fuses (or electronic fuses), and automotive fuses to suit the specific needs of different industries.
Based on size, fuses can be classified into large, medium, small and miniature fuses to suit different space and installation requirements.
According to the different rated voltages, fuses can be classified into high-voltage fuses, low-voltage fuses and safe voltage fuses to ensure that they can play a protective role in different voltage environments.
In terms of breaking capacity,circuit board fuse can be divided into two categories: high breaking capacity and low breaking capacity to meet the needs of different circuits for short-circuit current cutting capacity.
In terms of shape, fuses are available in a variety of designs, such as flat head tubular fuses (including internal and external welding), pointed tubular fuses, guillotine fuses, spiral fuses, inserted fuses, flat fuses, wrapped fuses, and patch fuses, etc., in order to adapt to different installation methods and space layout.
According to the melting speed, fuses can be divided into extra slow, slow, medium, fast and extra fast fuses to meet the requirements of different circuits for fault response time.
According to international standards, fuses can be divided into European, American and Japanese fuses to meet the market demand and safety standards in different regions.
In terms of type, fuses can be further classified into current fuses (such as chip fuses, miniature fuses, insert fuses, tubular fuses), temperature fuses (such as RH square type, RP resistor type, RY metal casing), and self-recovery fuses (including plug-in, laminated, patch and other forms).

In the circuit design of electronic equipment, the selection of circuit board fuse as an important safety component is of paramount importance. Elements of fuse selection:
1.Determine the operating current
The rated current of a fuse is the maximum value of current it can continuously carry at 25℃. However, in practice, in order to avoid the fuse blowing prematurely due to overheating, it is usually recommended to reduce the operating current to 75% of the rated current. For example, if the rated current of a fuse is 10A, the operating current should be no more than 7.5A at 25°C. In addition, the rated current of the fuse can also be selected with reference to 1.5-2.0 times of the actual input current of the product to ensure the safe operation of the circuit.
2.Confirm the voltage resistance value
The voltage withstand value of the fuse should be greater than or equal to the effective voltage of the circuit to ensure that it can function properly when the voltage is abnormal. Generally speaking, the commonly used fuse withstand voltage specification of 250V AC, but the specific selection should be based on the actual voltage of the circuit to determine.
3.Confirm the safety certification
Fuses should meet the relevant safety certification standards to ensure their quality and safety. Common safety certifications include IEC, UL, CSA, TUV, CCC and so on. When selecting a fuse, make sure it meets the required certification standards and check the relevant certificates and specifications.
4.Explore fuse test specifications
Test specifications vary for different types of fuses. For example, the IEC 127 standard covers a wide range of types such as tubular fuses, miniature fuses as well as surface mounted and perforated fuses. When selecting fuses, it is important to understand the test specification to which they belong and select the type in accordance with the actual application environment of the product.
5.Confirmation of Electrical Characteristics
The electrical characteristics of a circuit board fuse include the melting speed (fast blow, slow blow, self-recovery), surge (lightning strike) immunity, input inrush current and other relevant indicators.When selecting, it should be combined with the actual application environment of the product selection. For example, in switching power supplies,slow blow fuses are usually selected to cope with high overcurrent situations. At the same time, it is also necessary to consider whether the single pulse energy is less than the single pulse energy of the fuse to ensure that the fuse can blow normally under abnormal conditions.
6.Confirm the operating temperature range
The operating temperature range of the fuse should be greater than or equal to the actual product application temperature range. When selecting, you should know the operating temperature range of the printed circuit board fuses, and make sure it can meet the actual application requirements of the product.
7.Confirm the package form
Fuses are available in a variety of packages, including chip, insert, tube, etc. When selecting a fuse, it should be considered in the context of the product. In the selection, should be combined with the product volume, process, safety distance and cost and other factors for comprehensive consideration, choose the most appropriate fuse package form. At the same time, also need to pay attention to the electrical clearance and creepage distance before and after the fuse to ensure that the basic insulation requirements.
8.PCB board precautions
In PCB design, if the product needs to be certified, the specifications of the circuit board fuse (rated operating voltage and rated operating current) should be printed on the PCB. Even if the product does not require certification, it is recommended that the above information be marked simultaneously for subsequent maintenance and overhaul.
The correct selection and configuration of circuit board fuses is the key to ensure the safe and stable operation of electronic equipment.Comprehensive consideration of various factors, a reasonable choice of fuses,will provide solid protection for electronic equipment.