Rogers material is a specialised laminate used in the manufacture of high frequency, high performance Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) and is manufactured by Rogers Corporation. Rogers materials typically do not contain glass fibres, but rather a ceramic foundation or hydrocarbon ceramic composite substrate, which gives them excellent dielectric properties, low dielectric constants and low loss factors.
The materials are particularly suited for high-frequency electronic applications such as radio frequency (RF), microwave and high-speed digital communications, where they effectively maintain signal integrity and reduce transmission losses. Rogers materials also offer excellent thermal stability and mechanical strength, with coefficients of thermal expansion that are highly compatible with those of copper foils, ensuring the dimensional stability of circuits during temperature changes and avoiding damage and failures caused by thermal expansion and contraction.
Characteristics of Rogers materials
Low dielectric loss: Rogers materials have a low dielectric loss, which means that in high frequency applications it is possible to reduce energy loss during signal transmission and improve circuit performance.
High Frequency Performance: Rogers PCBs excel in high frequency applications, providing stable signal transmission and low attenuation in RF and microwave applications.
Thermal Stability: Rogers materials have good thermal stability and high temperature resistance, making them suitable for electronic equipment operating in high temperature environments.
Mechanical Strength: Rogers PCBs have high mechanical strength and impact resistance for applications requiring high reliability and durability.
Excellent processing performance: The material can easily cope with a variety of complex processing treatments, including drilling and assembly, making it ideally suited for the production of complex microwave and RF circuits. In addition, its excellent solderability makes connections to a wide range of metal joints a breeze.
Because of these features, Rogers PCBs are widely used in wireless communications, satellite systems, radar, high-speed data transmission, and aerospace, especially in circuit designs that require high-frequency performance and thermal stability.

FR-4 is a commonly used PCB substrate material, which stands for Flame Retardant Class 4 glass fibre reinforced epoxy resin material.FR-4 Class 4: FR-4 is classified into different classes, where Class 4 represents a material with high flame retardant properties. According to the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standard, FR-4 grade 4 means that the vertical burning rate of the material is less than or equal to 30 mm/min. FR-4 grade 4 materials are more reliable in terms of flame retardancy, and are widely used in the manufacture of electronic equipment. Therefore, the term FR-4 is an abbreviation for a class of glass fibre reinforced epoxy resin materials, which are a common and reliable PCB substrate material with good flame retardant properties. Due to its stable performance and relatively low production cost, FR-4 material is widely used in the manufacture of most general electronic equipment.
FR-4 material properties:
- High mechanical strength: glass fibre reinforcement gives FR-4 substrates excellent bending and impact resistance, able to withstand the stress brought about by complex circuit layouts.
- excellent electrical properties: FR-4 material has good electrical insulation properties, can effectively prevent the interference between different circuits on the circuit board and short circuit, to ensure the stability and reliability of signal transmission.
- Good flame retardant properties: UL94 V-0 level of flame retardant properties, so that the FR-4 material can be quickly self-extinguishing in the event of fire, greatly enhancing the safety of electronic products.
- Good processing performance: FR-4 material is easy to drill, cut, bend and other processing operations, suitable for the realisation of complex multi-layer board structure.
- Moderate cost: Compared with other high-performance materials, FR-4 materials have relatively low manufacturing costs and are suitable for mass production.
Why is Rogers better than FR4?
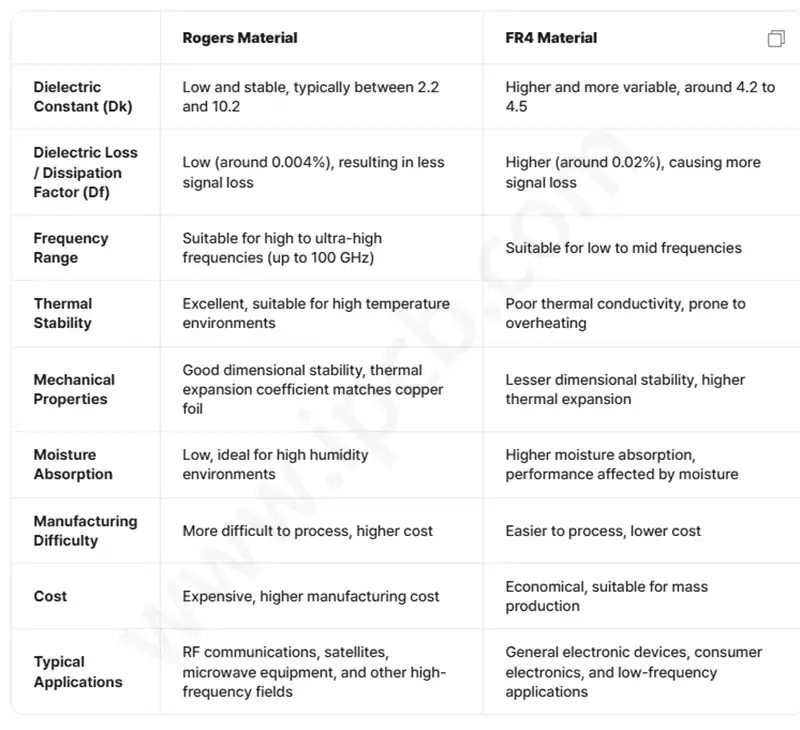
Dielectric constant (Dk)
Rogers material: The dielectric constant is low and stable, usually between 2.2 and 10.2, which is suitable for high frequency and high speed signal transmission to ensure signal integrity and impedance stability.
FR4 material: Higher dielectric constant and greater variation with frequency, usually between 4.2 and 4.5, prone to distortion and impedance instability during signal transmission, limiting its use in high-frequency applications.
Dielectric Loss/Dissipation Factor (Df)
Rogers materials: Low dissipation factor (about 0.004%) results in significantly lower signal loss, making them suitable for high-frequency, high-speed data transmission, such as RF communications and radar systems.
FR4 materials: Because of the high dissipation factor (approx. 0.02%), it results in high loss during signal transmission, affecting signal quality and is not favourable for high-frequency applications.
Frequency application range
Rogers materials: designed for UHF applications, the upper frequency limit can reach 100 GHz, which greatly meets the needs of complex high-speed, high-frequency communications.
FR4 material: applicable mainly to low and medium frequency applications, generally used in general electronic equipment, poor performance under high frequency conditions.
Thermal Stability
Rogers materials: excellent thermal performance, able to maintain stable electrical performance in high-temperature environments, and through good thermal conductivity to help dissipate heat and ensure work reliability.
FR4 materials: poor thermal conductivity, can not effectively dissipate heat, in high power or high temperature application environment easily lead to circuit failure.
Mechanical Properties and Dimensional Stability
Rogers material: good dimensional stability, coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) matches copper foil, reducing mechanical stress caused by thermal expansion and contraction, and improving circuit board reliability.
FR4 material: larger coefficient of thermal expansion, dimensional stability is poor, easy to deformation due to temperature changes, affecting circuit performance and life.
Moisture absorption rate
Rogers material: moisture absorption rate is very low, suitable for high humidity, high temperature harsh environment, to ensure the stability of electrical characteristics.
FR4 material: relatively high moisture absorption rate, easy to absorb water leading to performance degradation, limiting the application in some environments.
Processing difficulty and cost
Rogers material: due to the physical properties of more fragile and precision, manufacturing and processing difficulties, higher prices, suitable for the requirements of high performance, high reliability of the professional field.
FR4 materials: Mature processing, low manufacturing costs, suitable for mass production and general electronic applications.
The use of Rogers material instead of FR4 material is mainly based on the demand for high-frequency low loss, dimensional stability, thermal management and environmental adaptability. Although Rogers materials are more costly, they ensure stable operation of high-performance circuits and are ideal for application scenarios with high performance requirements. FR4, on the other hand, remains the mainstream material for general electronics due to its low cost and good mechanical strength.