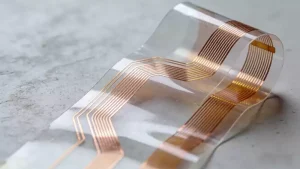
FPC Dielectric Loss Challenges and Solutions in High Frequency
With the widespread adoption of 5G communications and IoT technologies, electronic devices are rapidly evolving toward higher frequency operation, placing greater demands on the dielectric properties of FPC materials. In
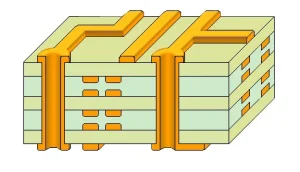
Dielectric Constant and Capacitance: Key Factors in High-Speed PCB Design
The Fundamental Relationship Between Dielectric Constant and Capacitance in PCB Design In electronic circuit design, the relationship between dielectric constant and capacitance is one of the fundamental concepts for understanding
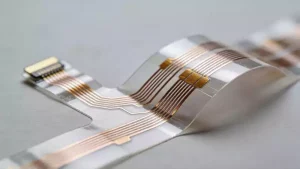
FPC Antennas Principles and Manufacturing Processes
FPC antennas, formally known as flexible printed circuit antennas, are specialised antennas that integrate key functional components such as the antenna radiation unit and feed structure onto a flexible PCB

Assembly Challenges of Flexible Antennas
The fundamental challenge in assembling flexible antennas lies in the contradiction between “physical flexibility” and “assembly precision.” The substrate is extremely thin—almost paper-like—yet it must support micron-level alignment accuracy. The

Core Analysis of FPC Antennas
As electronic devices continue to evolve toward thinner profiles, higher frequencies, and greater functionality, antenna design faces a critical challenge: extreme space constraints without compromising performance. FPC antennas have emerged
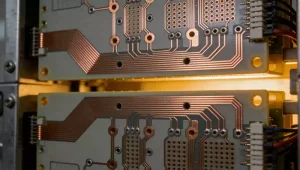
Selection of FR4 PCB Materials for Different Layer Counts
In printed circuit board (PCB) material selection, FR4 is one of the most widely used substrates. However, even within the FR4 category, single-sided, double-sided, and multilayer structures differ significantly in

Selection of FR4 Material for High Voltage Circuits
In high-voltage PCB design, the insulation performance of FR4 materials directly affects the safety and stability of circuits. Among the relevant parameters, tracking resistance indicators are an important reference for

Differences in Frequency Bands for Automotive Radar PCB Antenna Design
All design differences between 24 GHz and 77 GHz automotive radar PCB antenna boards fundamentally stem from the distinct physical characteristics of the frequency bands themselves. Frequency determines wavelength, and

The Critical Role and Design Considerations of PCB Antenna Ground Planes
In wireless communications, antennas are of paramount importance, and the PCB antenna ground plane, as a critical component, influences multiple aspects of antenna performance. In wireless communications, pcb antennas are

Application of Serpentine Antennas in Small Wearable Devices
Inside products such as smart bands, TWS earbuds, smartwatches, and health monitoring patches, there is a constant tension between extremely limited internal space and ever-increasing communication requirements. Serpentine antennas, with

Key Considerations for EMC Design of Antenna PCB
In antenna PCB design, electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is a key factor in ensuring stable device performance and minimizing interference. As core elements of EMC design, layout and routing are not
Four layer flexible circuit board
What is a four layer flexible board? FPC flexible boards can be used to manufacture four layer boards, but compared to double-layer or multi-layer FPC flexible boards, the manufacturing process

Selection of Rogers and FR-4 Substrates for Antenna pcb
FR-4 and Rogers, as the two most prevalent substrate materials in the antenna PCB sector, possess no inherent superiority or inferiority; their suitability depends solely on the application context. Selecting

Optimisation of the Solder Mask Layer for High Frequency Antennas
A high frequency antenna operates in the 300 MHz–300 GHz RF spectrum (corresponding to electromagnetic wavelengths of 1 m–1 mm). It is the core RF component responsible for bidirectional energy

Cost and Performance Comparison of PCB Antennas versus Ceramic Antennas
PCB antennas are directly formed by etching metal traces on the PCB substrate to create radiation units, utilizing the rigid material of the PCB for signal transmission and reception, without

Controlling Drilling Damage in FR4 Substrates to Enhance PCB Quality
Mechanical drilling constitutes the core process for achieving interlayer electrical interconnections in PCBs, yet it remains the stage where FR4 substrates are most susceptible to microscopic damage. Under the combined

Why FR4 Plate Keyboards Are Gaining Popularity in Custom Mechanical Designs
The Role of FR4 Plate Keyboard in Mechanical Keyboard Structure In the structural design of mechanical keyboards, the plate (positioning plate) is a crucial intermediate layer connecting the switches to

Differences and Selection Between Aluminide and Alumina Ceramic Substrates
Ceramic substrates, as critically important materials within PCBs, play a pivotal role in enhancing PCB performance through their unique physical and chemical properties. Among these, aluminium oxide (Al₂O₃) and aluminium

4 layer PCB Layering Techniques for Achieving Extremely Low Noise Routing
As one of the most widely adopted specifications in the industry, the cost-effectiveness and practicality of 4 layer PCBs are beyond question. However, achieving low noise floor hinges not on
Via Form and Cost in PCB boards
PCB boards serving as the core carriers of electronic devices, see their performance and cost directly influenced by the precision of their design and manufacture. Via holes, as the fundamental

Ultra Thin PCBs Drive the Advancement of Wearable Devices
In recent years, the widespread adoption of smart wearable devices has significantly transformed people’s lifestyles and health management. From smartwatches and fitness trackers to smart glasses and medical devices, wearables

Why is PCB layout more decisive than routing in PCB design?
In the complex process of PCB design, PCB layout and PCB routing are two core stages that together determine the final performance and reliability of the product. However, during the

High Frequency Board Technology for 5G Base Stations
In the current era where 5G communication technology is reshaping the global information landscape with lightning speed, 5G base stations, serving as the “nerve endings” of network coverage, directly determine

4 layer PCB High-Efficiency Heat Dissipation Design Strategy
In the era where electronic devices are constantly evolving towards higher performance and greater integration, the heat dissipation issue of PCBs has become increasingly critical. Copper, with its outstanding thermal